Prophylactic Antibiotics in Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: A Nationwide Analysis of Infection Rates and Antibiotic Use in South Korea
- PMID: 41009880
- PMCID: PMC12466463
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14090901
Prophylactic Antibiotics in Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: A Nationwide Analysis of Infection Rates and Antibiotic Use in South Korea
Abstract
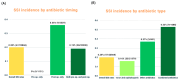
Background/Objectives: Vertebroplasty (VP) and kyphoplasty (KP) are widely performed minimally invasive procedures for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and vertebral metastases. Although generally safe, postoperative surgical site infections (SSIs) can lead to severe complications. The true incidence of SSIs and optimal prophylactic antibiotic strategies remains unclear. This study evaluated SSI incidence and the impact of antibiotic timing and type using a nationwide quality assessment (QA) database in South Korea. Methods: We analyzed data from the 7th to 9th QA waves of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) Service, including 23,868 patients who underwent VP or KP. SSI incidence was compared across antibiotic timing groups (preoperative-only, postoperative-only, and combined) and antibiotic types. Multivariate logistic regression identified independent risk factors for SSIs. Results: SSI occurred in 47 patients (0.20% of 23,868 procedures). No infections were observed in the preoperative-only group, compared with 0.36% in the postoperative-only group and 0.19% in the pre- and postoperative group. The lowest incidence (0.16%) was seen with first- or second-generation cephalosporins. Multivariate analysis found no significant difference between the preoperative-only and the combined regimens, nor between first-/second-generation cephalosporins and broad-spectrum antibiotics. However, surgery at a tertiary hospital (aOR: 3.566) and malnutrition (aOR: 2.915) were independently associated with increased SSI risk. Conclusions: This nationwide study, the largest to date on VP and KP, demonstrated that SSIs are rare (0.2%). A single preoperative dose of first- or second-generation cephalosporins was as effective as combined or broader-spectrum regimens. Targeted preventive measures may be warranted for high-risk groups such as patients with malnutrition or those treated in tertiary hospitals.
Keywords: antibiotic prophylaxis; kyphoplasty; spine surgery; surgical wound infection; vertebroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bae J.W., Gwak H.S., Kim S., Joo J., Shin S.H., Yoo H., Lee S.H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for patients with metastatic compression fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: Clinical and radiological factors affecting functional outcomes. Spine J. 2016;16:355–364. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.11.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li H., Zou J., Yu J. Effect of Robot-Assisted Surgery on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures after Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation: A Meta-Analysis and a Validation Cohort. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2024;16:948–961. doi: 10.4055/cios24086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mattie R., Laimi K., Yu S., Saltychev M. Comparing Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Therapy for Treating Osteoporotic Compression Fractures in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016;98:1041–1051. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.15.00425. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Halvachizadeh S., Stalder A.L., Bellut D., Hoppe S., Rossbach P., Cianfoni A., Schnake K.J., Mica L., Pfeifer R., Sprengel K., et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 3 Treatment Arms for Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Comparison of Improvement in Pain, Adjacent-Level Fractures, and Quality of Life Between Vertebroplasty, Kyphoplasty, and Nonoperative Management. JBJS Rev. 2021;9:e21. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.21.00045. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

