Feasibility Evaluation of Partially Replacing Ordinary Portland Cement with Ferro-Nickel Slag in Ready-Mixed Concrete for Precast Applications
- PMID: 41010159
- PMCID: PMC12471512
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18184315
Feasibility Evaluation of Partially Replacing Ordinary Portland Cement with Ferro-Nickel Slag in Ready-Mixed Concrete for Precast Applications
Abstract
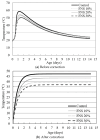
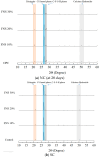
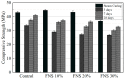
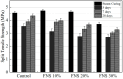
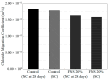
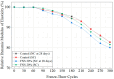
The global generation of industrial waste is increasing rapidly, with much of it either landfilled or discharged into marine environments, resulting in severe environmental pollution. To address this issue, extensive research has been conducted on utilizing waste materials as partial replacements for cement. Although concrete incorporating industrial by-products offers environmental advantages-such as reducing pollution and lowering CO2 emissions-its application has been limited by poor early-age performance. In South Korea, the annual production of ferronickel slag (FNS) now exceeds 2,000,000 tons, yet its usage remains minimal. To improve this early-age performance, researchers have applied steam curing (SC), a method widely used in precast concrete, which can enhance the utilization of FNS-containing concrete. Some studies have individually evaluated the mechanical or microstructural properties of SC effects, but the combined effects of FNS and SC replacement in precast concrete have rarely been addressed. This study applied SC, a method widely used in precast concrete production, to improve the performance of FNS concrete and conducted a comprehensive evaluation to promote its practical application. For this purpose, ordinary Portland cement (OPC) was partially replaced with FNS at rates of 10%, 20%, and 30%. To assess the effects, tests were conducted on hydration heat, SEM, and XRD, along with evaluations of compressive and splitting tensile strength. Results identified 20% as the optimal replacement ratio. At this ratio, chloride penetration resistance and freeze-thaw durability were also assessed. Furthermore, FNS concrete was evaluated under both natural curing (NC, 28 days) and SC conditions to simulate precast production. Under NC, mechanical properties declined as the FNS content increased, whereas under SC, the performance of the 20% replacement mixture was comparable to that of the control. In addition, the chloride diffusion coefficient and freeze-thaw resistance were improved by 11% and 2%, respectively, under SC compared to NC. This study evaluated the feasibility of FNS-containing concrete, and further studies should be conducted to investigate the structural performance of FNS-containing reinforced concrete via methods such as flexural, shear, splicing, and debonding experiments.
Keywords: eco-friendly; ferro-nickel slag; industrial waste; precast; steam curing.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jin-Su Kim is student in the Yonsei University; author Jun-Pil Hwang is CEO in the CMME; author Chang-Hong Lee was employed in Posco E & C Co., Ltd.; author Jang-Ho Jay Kim was employed in the Yonsei University. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Khankhaje E., Kim T., Jang H., Kim C.S., Kim J., Rafieizonooz M. A review of utilization of industrial waste materials as cement replacement in pervious concrete: An alternative approach to sustainable pervious concrete production. Heliyon. 2024;10:e26188. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohamad N., Muthusamy K., Embong R., Kusbiantoro A., Hashim M.H. Environmental impact of cement production and Solutions: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022;48:741–746. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.212. - DOI
-
- Amran M., Murali G., Khalid N.H.A., Fediuk R., Ozbakkaloglu T., Lee Y.H., Haruna S., Lee Y.Y. Slag uses in making an ecofriendly and sustainable concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;272:121942. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121942. - DOI
-
- Ahmad J., Kontoleon K.J., Majdi A., Naqash M.T., Deifalla A.F., Ben Kahla N., Isleem H.F., Qaidi S.M. A comprehensive review on the ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) in concrete production. Sustainability. 2022;14:8783. doi: 10.3390/su14148783. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

