Finerenone Versus Placebo on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 41010560
- PMCID: PMC12470496
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14186355
Finerenone Versus Placebo on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
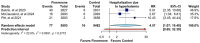
Background/Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of finerenone compared to placebo in improving renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted, compiling RCTs evaluated the effect of finerenone compared to placebo in patients with CKD and T2D. Inclusion criteria included adults with CKD and T2D. Outcomes included kidney failure, end-stage renal disease (ESKD), and persistently decreased glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Secondary outcomes included cardiovascular events, hospitalization due to hyperkalemia, and serious adverse events. Pooled relative risks (RRs) and mean differences (MDs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Results: Three RCTs with a total of 19,027 patients were included. Finerenone demonstrated a potential reduction in kidney failure risk (RR 0.86, 95% CI: 0.35-2.13) and ESKD (RR 0.82, 95% CI: 0.54-1.23); however, confidence intervals included the null effect. There were no statistically significant differences, as seen in the decrease in eGFR (RR 1.03; 95% CI: 0.27-3.85), but also in mortality due to renal causes (RR 0.62; 95% CI: 0.00-7168.81). Finerenone increased hyperkalemia-related hospitalizations (RR 4.57, 95% CI: 1.07-19.48) but had no significant effect on serious adverse events (RR 0.94, 95% CI: 0.92-0.97) or systolic BP (MD 0.08 mmHg, 95% CI: -0.36 to 0.52). Conclusions: Finerenone may provide renal protection in CKD and T2D, though benefits remain uncertain due to wide confidence intervals and study heterogeneity. The increased risk of hyperkalemia warrants careful patient selection and monitoring. Further research is needed to refine its clinical applicability. Review registration: PROSPERO CRD420250642593.
Keywords: cardiovascular outcomes; chronic kidney disease; finerenone; meta-analysis; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
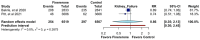



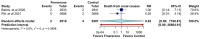

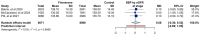
References
-
- Calvo-Hueros J.I., Martín-Hidalgo-Barquero M.V., Morales-Gabardino J.A., Buitrago F. Chronic kidney disease prevalence and cardiovascular risk in a cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes followed for 10 years in Badajoz (Spain). An observational study. Prim. Care Diabetes. 2021;15:391–396. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2020.11.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

