Research Progress on Chemical Components of Astragalus membranaceus and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome
- PMID: 41011612
- PMCID: PMC12472940
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30183721
Research Progress on Chemical Components of Astragalus membranaceus and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
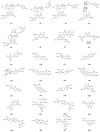
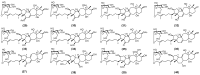
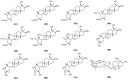
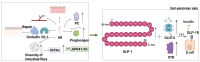
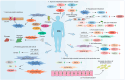
Astragalus membranaceus (AM), also known as Huangqi in Chinese, refers to the dried root of two Leguminosae species: AM (Fisch.) Bge. and its variety AM (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. In recent years, research on AM has been published in many papers. Its role in treating metabolic syndrome (MetS) has attracted increasing attention. This review summarizes the research progress over the past five years on the chemical constituents of AM and its therapeutic potential in MetS-related diseases. Chemical analyses of AM have gradually expanded from its roots to its stems, leaves, and entire plant. The major compounds isolated from AM include flavonoids, saponins, and polysaccharides. Extraction methods include ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry and in vitro intestinal absorption models combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array-tandem mass spectrometry. AM and its active components exert beneficial effects on metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. These effects are achieved mainly through mechanisms such as reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, modulating gut microbiota, regulating lipid metabolism, improving insulin resistance, and protecting pancreatic β-cell function. This review provides a reference for further studies on treatment of MetS of AM.
Keywords: Astragalus membranaceus; cardiovascular diseases; chemical constituents; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. China Medical Science Press; Beijing, China: 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

