mRNA and DNA-Based Vaccines in Genitourinary Cancers: A New Frontier in Personalized Immunotherapy
- PMID: 41012105
- PMCID: PMC12474112
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13090899
mRNA and DNA-Based Vaccines in Genitourinary Cancers: A New Frontier in Personalized Immunotherapy
Abstract
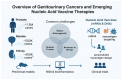
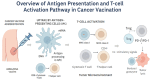
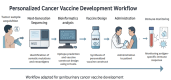
Genitourinary (GU) cancers, including prostate, bladder, and renal cancers, represent a significant burden on global health. Conventional treatments, while effective in certain contexts, face limitations due to tumor heterogeneity, therapeutic resistance, and relapse. Recent advances in cancer immunotherapy, particularly in the development of personalized mRNA and DNA-based vaccines, have opened new avenues for precise and durable antitumor responses. These vaccines are being developed to leverage neoantigen identification and next-generation sequencing technologies, with the goal of tailoring immunotherapeutic interventions to individual tumor profiles. mRNA vaccines offer rapid, non-integrative, and scalable, with encouraging results reported in infectious diseases and early-phase cancer trials. DNA vaccines, known for their stability and ease of modification, show promise in generating robust cytotoxic T-cell responses. This review discusses the current landscape, preclinical findings, and ongoing clinical trials of mRNA and DNA-based vaccines in GU cancers, highlighting delivery technologies, combination strategies with immune checkpoint inhibitors, and future challenges, including tumor immune evasion and regulatory hurdles. Integrating immunogenomics and artificial intelligence into vaccine design is poised to further enhance precision in cancer vaccine development. As GU malignancies remain a leading cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality, mRNA and DNA vaccine strategies represent a promising and rapidly evolving area of investigation in oncology.
Keywords: DNA vaccines; bladder cancer; genitourinary cancer; immunotherapy; mRNA vaccines; neoantigens; personalized cancer vaccine; prostate cancer; renal cell carcinoma; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Gabriela Barbosa and Leonardo O. Reis (coordinator) are members of the INCT UroGen, the National Institute of Science, Technology, and Innovation in Genitourinary Cancer (INCT). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

