CXCR5 Signals Fine-Tune Dendritic Cell Transcription and Regulate TH2 Development
- PMID: 41012147
- PMCID: PMC12474269
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13090943
CXCR5 Signals Fine-Tune Dendritic Cell Transcription and Regulate TH2 Development
Abstract
Background/objectives: We previously demonstrated that dendritic cell (DC) expression of CXCR5 is required for TH2 priming in mice infected with the helminth Heligmosomoides polygyrus (Hp). In this manuscript we examined how CXCR5 controls DC mediated CD4 T helper 2 cell (TH2) development.
Methods: We used in vitro TH2 priming assays, RNA-seq analyses and in vivo Hp infection mouse models to identify roles for the CXCR5-expressing DCs in TH2 development.
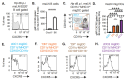
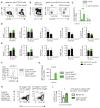
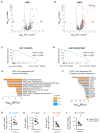
Results: We showed that migratory conventional type 2 dendritic cells (cDC2) express CXCR5 and that deletion of Cxcr5 prevents migratory DC priming of TH2 cells in vitro while overexpression of CXCR5 enhances migratory DC priming of TH2 cells in vitro. To understand how CXCR5 facilitates the TH2 priming capabilities of migratory cDC2 cells, we performed RNAseq analysis on wildtype and Cxcr5-/- DC subsets isolated from msLN of Hp-infected mice. We observed that CXCR5 expression specifically by the migratory cDC2 subset promoted a pro-proliferative transcriptional program in cDC2 cells and was required for cDC2 cell accumulation in the msLN following Hp infection. We demonstrated that CXCR5 expression specifically by cDC2 cells was necessary for upregulation of Chitinase 3-like-1 (Chi3l1), which encodes a secreted protein (Chi3l1) that regulates allergic TH2 responses. We showed that addition of recombinant Chi3l1 protein to in vitro TH2 priming cultures enhanced TH2 development and that deletion of Chi3l1 specifically in DCs resulted in fewer cDC2 cells and decreased TH2 development in vivo following Hp infection.
Conclusions: CXCR5 expressed by cDC2 cells is required for induction of Chi3l1, which in turn promotes the TH2 priming capacity of these DCs. These findings provide insight into the actions of CXCR5 and Chi3l1 in helminth infection.
Keywords: CXCR5; Chi3l1; TH2 responses; dendritic cells; helminth infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

