Clinical, Psychosocial, and Structural Factors Associated with the Detection of HIV Drug Resistance in Children Living with HIV in Kisumu, Kenya: Secondary Analysis of Data from the Opt4Kids Study
- PMID: 41012674
- PMCID: PMC12474375
- DOI: 10.3390/v17091246
Clinical, Psychosocial, and Structural Factors Associated with the Detection of HIV Drug Resistance in Children Living with HIV in Kisumu, Kenya: Secondary Analysis of Data from the Opt4Kids Study
Abstract
Background: HIV drug resistance (DR) mutations can compromise antiretroviral therapy (ART) success among children living with HIV (CLHIV). We conducted a secondary analysis using data from a randomized control trial for ART monitoring among CLHIV in Kisumu County, Kenya from 2019 to 2023, to assess clinical, psychosocial, and structural factors associated with HIV DR.
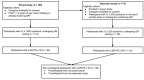
Methods: 704 CLHIV were followed for 12+ months, with characteristics captured at enrollment and follow-up visits in the "parent" randomized-controlled-trial (of point-of-care plasma viral load testing and for viremias ≥ 1000 copies/mL HIV genotyping for DR vs. standard-of-care) and an observational "extension" substudy (of participants on a dolutegravir-containing ART with genotyping performed on viremic specimens ≥ 200 copies/mL). A multivariate modified Poisson regression model was used to analyze factors associated with sequences yielding a Stanford HIVDR database DR penalty score (DR-PS) ≥ 30 to a nucleos(t)ides and/or non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, protease inhibitor (PI), and/or integrase inhibitor (INSTI).
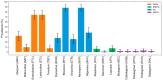
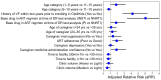
Results: Among 113 (16.1%) participants who underwent genotyping, 93 (82.3%) had a DR-PS ≥ 30. DR-PS ≥ 30 were associated with age 1-5 years (adjusted risk ratio (ARR) = 1.84; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.07, 3.14), history of viremia ≥ 1000 copies/mL (ARR = 4.18; 95% CI: 2.77, 6.31), prescription of a PI- (ARR = 6.05; 95% CI: 3.43, 10.68) or INSTI-containing regimen (ARR = 1.83; 95% CI: 1.08, 3.11), poor adherence to ART (ARR = 1.91; 95% CI: 1.32, 2.76), lack of caregiver confidence in ART administration (ARR = 1.89; 95% CI: 1.11, 3.22), and mid-sized clinic populations (ARR = 0.55; 95% CI: 0.33, 0.92).
Conclusion: Addressing social factors associated with DR-PS ≥ 30 may improve ART success among CLHIV.
Keywords: HIV; Kenya; children; drug resistance mutation (DRM); viral failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF Global and Regional Trends. [(accessed on 18 August 2025)]. Updated July 2025. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/hivaids/global-regional-trends/
-
- Han W.M., Law M.G., Egger M., Wools-Kaloustian K., Moore R., McGowan C., Kumarasamy N., Desmonde S., Edmonds A., Davies M.-A., et al. Global estimates of viral suppression in children and adolescents and adults on antiretroviral therapy adjusted for missing viral load measurements: A multiregional, retrospective cohort study in 31 countries. Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e766–e775. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00265-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS Kenya HIV and AIDS Estimates. [(accessed on 18 August 2025)]. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/kenya.
-
- Mulinge M.M., Kibui N.K., Kimani H., Wainaina J., Bwana P., Omondi M., Wafula K., Wamalwa D.C., Omondi E.O., Nduati R.W., et al. Factors associated with viral load non-suppression among treatment-experienced pre-teenage children living with HIV in Kenya: A nationwide population-based cohort study, 2015–2021. eClinicalMedicine. 2024;68:102454. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102454. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS New High-Quality Antiretroviral Therapy to be Launched in South Africa, Kenya and over 90 Low-and Middle-Income Countries at Reduced Price. [(accessed on 20 July 2025)]. Published 21 September 2017. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/pressreleaseandstatement....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

