Radiomics-Based Prognostication in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Proof-of-Concept Study
- PMID: 41014131
- PMCID: PMC12476022
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70348
Radiomics-Based Prognostication in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
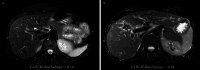
Background and aim: Risk assessment in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) relies on semi-quantitative analysis, which can result in interpretation variability. Radiomics may offer a quantitative approach for risk stratification. This study aims to explore and validate MRI-derived radiomic features to identify high-risk PSC patients.
Methods: In this prospective study (January 2019-December 2022), consecutive PSC patients undergoing routine gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI were recruited. Using PyRadiomics, whole liver parenchyma features were extracted from five MRI sequences according to the Image Biomarker Standardisation Initiative (IBSI). Patients were categorised into risk groups based on the Mayo risk score (MRS) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM). Features associated with high-risk patients were selected and validated in an independent cohort. A survival analysis was conducted in the combined cohort to assess the prognostic value of the radiomic features for clinical events.
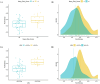
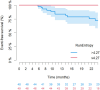
Results: One hundred and two PSC patients were enrolled in this study. Five radiomics features were associated with high risk in the training cohort. In the validation setting, GLRLM-Run Entropy in the fat-saturation T2 weighted imaging (FS-T2W) sequence was the only significant feature, with an odds ratio of 3.90 (CI 1.46-10.42, p = 0.007) for MRS and 2.97 (CI 1.33-6.66, p = 0.008) for LSM. Its prognostic potential on clinical outcome was confirmed by Cox regression analysis in the combined cohort (hazard ratio per 0.1 increase = 1.480, CI 1.226-1.786), showing excellent predictive performance (C-index = 0.857).
Conclusions: GLRLM-Run Entropy in FS-T2W is a novel radiomics-based biomarker for risk stratification in PSC patients. It is quantitative, standardised, easy to compute and cost-free, positioning it as a potential key innovation in PSC radiology-based biomarkers.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrial.gov ID: NC705618145.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; autoimmune liver diseases; quantitative radiology; radiomics; risk stratification; surrogate biomarkers.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Data Transparency Statement: Deidentified individual participant data that underlie the reported results will be made available 3 months after publication for a period of 5 years. Proposals for access should be sent to
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- “Introduction to Radiomics” (2020), 10.2967/jnumed.118.222893. - DOI
-
- Cazzagon N., El Mouhadi S., Vanderbecq Q., et al., “Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Metrics Are Associated With Disease Severity and Outcomes in People With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis,” JHEP Reports 4, no. 11 (2022): 100577, 10.1016/J.JHEPR.2022.100577. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

