TELLBASE: a novel tool of TELL-seq barcode-assisted scaffold assembler for bacterial genomes
- PMID: 41016011
- PMCID: PMC12476840
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbaf504
TELLBASE: a novel tool of TELL-seq barcode-assisted scaffold assembler for bacterial genomes
Abstract
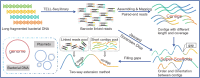
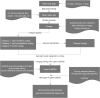
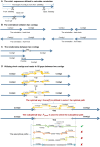
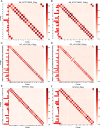
Transposase enzyme linked long-read sequencing (TELL-seq) technology generates barcode-linked reads, facilitating whole-genome sequencing (WGS), and complete assembly with improved accuracy and reduced costs. Unlike mate-pair sequencing technology, TELL-seq employs a near-full-sequence tagging strategy that allows more efficient capture of comprehensive genomic information. However, assembly algorithms and software capable of fully leveraging the characteristics of TELL-seq technology to effectively assemble genomic sequences at the megabase-scale are lacking, particularly for bacteria and their plasmids. In this study, we present TELL-seq barcode-assisted scaffold assembler (TELLBASE), a de novo genome assembler designed specifically for assembling bacterial genomes using TELL-seq-derived linked reads. In assembly tests involving bacteria such as Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Staphylococcus aureus, TELLBASE exhibited exceptional efficacy in producing chromosome-level bacterial genomic sequences and successful identification of plasmids present in the sequenced strains. Comparative analysis revealed that TELLBASE significantly outperforms existing assemblers tailored for TELL-seq-derived linked reads, such as TuringAssembler and Ariadne, in terms of the completeness and accuracy of the assembled genomes. Therefore, TELLBASE shows promising potential for refining draft bacterial genomes and further applications in related fields. The package for TELLBASE is freely available on GitHub (https://github.com/sosie1/TELLBASE).
Keywords: assemble algorithm for TELL-seq platform; bacterial genome assembly; barcoded NGS for bacterial genome; complete de novo assembly.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

