Ethambutol optic neuropathy
- PMID: 41018187
- PMCID: PMC12460111
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1626909
Ethambutol optic neuropathy
Abstract
Ethambutol is an antitubercular drug that is commonly used in the areas of the world that is endemic to tuberculosis. It is used in infections caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and some non-tuberculous infections caused by Mycobacterium species. Ethambutol related toxic optic neuropathy remains one of the most concerning adverse effects of the medication in addition to other non-specific side effects like peripheral neuropathy, nausea, vomiting, joint pain and rash. Recently the guidelines for treatment of tuberculosis in some countries where tuberculosis (TB) is endemic have been revised to allow for fixed dose combinations (wherein a single tablet contains a fixed strength of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) and longer duration of treatment with ethambutol. Thus, it is anticipated that there will be an increase in ethambutol toxic optic neuropathy. In this minireview we plan to discuss the clinical features, neuro-ophthalmic evaluation, screening and diagnosis of ethambutol toxic optic neuropathy. We will also discuss the available treatment options for this condition.
Keywords: antitubercular therapy; arabinosyl transferase; ethambutol; mycobacteria; optic neuropathy.
Copyright © 2025 Sudhakar, Acharya and Kini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


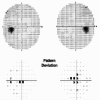

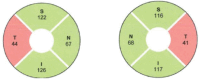
References
-
- Carr RE, Henkind P. Ocular manifestations of ethambutol. Arch Ophthalmol. (1962) 67:566–71. - PubMed
-
- Harada I. Two cases of neuritis retrobulbaris due to orally administered ethambutol. Nihon Ganka Kiyo. (1963) 14:278–84. - PubMed
-
- Tripathi KD. Antitubercular drugs essential of medical pharmacology. 7th ed. Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd., India; (2013). 765 p.
-
- Chan RY, Kwok AK. Ocular toxicity of ethambutol. Hong Kong Med J. (2006) 12:56–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

