Dehydrozaluzanin C inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and cycle arrest through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) activation
- PMID: 41019996
- PMCID: PMC12461092
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1623153
Dehydrozaluzanin C inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and cycle arrest through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) activation
Abstract
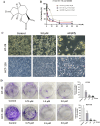
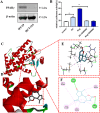
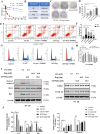
Dehydrozaluzanin C (DC) is a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Asteraceae plant Ainsliaea macrocephala. To investigate the antitumor effects of DC and possible molecular mechanisms for treating cancer. The antitumor effect of DC was studied using HT-29 and HCT-116 human colon tumor cell lines and Balb/c nude mice models. The anti-proliferative, proapoptotic effects, and cycle arrest of DC were observed by cell viability, colony formation, apoptosis, and cycle assays. The changes of protein expression level were examined by Western blot analysis. The transcription activity of PPARγ was determined by Luciferase reporter assay. The role of PPARγ activation in the antitumor activity of DC was verified using PPARγ antagonist GW9662 and si-PPARγ HT-29 cells. DC treatment significantly decreased colon tumor cell viability, cell clone number, and increased apoptosis rate and arrested cell cycle at S phase. Furthermore, DC treatment significantly decreased Bcl-2, CDK2, and cyclin A2 protein levels while increasing the expression of cleaved caspase 3 and Bax in HT-29 and HCT-116 cells. Further investigations indicated that cell survival, induction of apoptosis, and cycle arrest by DC could be significantly reversed following treatment with the PPARγ antagonist GW9662 or in si-PPARγ cells. In vivo, DC treatment significantly decreased the weight and volume of xenograft tumor tissues in mice and apoptosis-related protein levels. The results suggest that DC effectively inhibits colon tumor cell proliferation, clone formation, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest through PPARγ activation. These results support the potential of DC as an anti-tumor lead compound for further investigation.
Keywords: Dehydrozaluzanin C; PPARγ activation; apoptosis induction; colon cancer; cycle arrest.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li, Zhu, Li, Xu, Zu, Li and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chen X.-X., Khyeam S., Zhang Z.-J., Zhang K.Y.-B. (2022). Granatin B and punicalagin from Chinese herbal medicine pomegranate peels elicit reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Phytomedicine 97, 153923. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153923 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

