Autonomic dysregulation and atrial arrhythmias
- PMID: 41021733
- PMCID: PMC12559890
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00537.2025
Autonomic dysregulation and atrial arrhythmias
Abstract
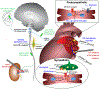
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) and its dysregulation are recognized as important mechanisms underlying atrial arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AF). In this review, we describe the anatomy of the cardiac nervous system, sympathetic and parasympathetic effects on atrial electrophysiology, and how dysregulation of those may predispose to AF initiation and promote its maintenance. We then discuss how the ANS itself undergoes functional and structural remodeling in the setting of atrial arrhythmias, and what are the current neuromodulation approaches for AF prevention and treatment. These strategies include destruction of cardiac ANS structures or modification of autonomic signaling using nerve stimulation, pharmacological or gene therapy. Autonomic mechanisms of AF have been a focus of basic and translational research for many years, and now with the development of new diagnostic tools and therapeutic methods, ANS-targeted approaches have a potential to become an important part of AF treatment.
Keywords: atrial arrhythmias; autonomic nervous system; electrophysiology.
Figures
References
-
- Taylor EW, Jordan D, Coote JH. Central control of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and their interactions in vertebrates. Physiol Rev 1999;79(3):855–916. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh A, Patel NJ, Nalluri N, et al. Trends in hospitalization for atrial fibrillation: epidemiology, cost, and implications for the future. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2015;58(2):105–116. - PubMed
-
- Buja A, Rebba V, Montecchio L, et al. The Cost of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review. Value Health. 2024;27(4):527–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

