Undiagnosed G6PD Deficiency in Black and Asian Individuals Is Prevalent and Contributes to Health Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis and Complications
- PMID: 41022122
- PMCID: PMC7618273
- DOI: 10.2337/dc25-0556
Undiagnosed G6PD Deficiency in Black and Asian Individuals Is Prevalent and Contributes to Health Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis and Complications
Abstract
Objective: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency presents silently and is not routinely screened. It is associated with markedly lower HbA1c for the prevailing glucose levels. Since HbA1c is internationally recommended to diagnose and manage type 2 diabetes (T2D), we investigated the population-level impact of undiagnosed G6PD deficiency on T2D diagnosis and complications in the U.K.
Research design and methods: We used whole-exome sequencing and electronic health record data from UK Biobank (n = 467,368) and Genes & Health (n = 43,011) cohorts.
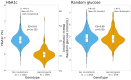
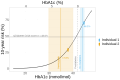
Results: In the U.K., we estimated that ∼1 in 7 Black and 1 in 63 Asian males carry G6PD deficiency alleles, compared with fewer than 1 in 10,000 White males. Despite this, less than 1 in 50 G6PD-deficient men are clinically recognized. Male G6PD carriers have considerably lower average HbA1c (0.9% [International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine: 10.0 mmol/mol]) compared with noncarriers, while differences in average glucose were negligible. G6PD-deficient men had 1.37 (95% CI: 1.01, 1.86) higher odds of developing diabetes-related microvascular complications than noncarriers. Although risk factors were similar prior to diagnosis, male G6PD carriers diagnosed with T2D since 2011 were, on average, 4.1 years (95% CI: 0.6, 7.7) older at diagnosis compared with noncarriers. In addition, lower mean HbA1c values in G6PD carriers falsely underestimated their 10-year T2D risk.
Conclusions: Undiagnosed G6PD deficiency has significant impact on T2D diagnosis with HbA1c and associates with increased risk of diabetes complications. This has major implications for global populations using HbA1c for diagnosis and monitoring, and could contribute significantly to inequalities in diabetes outcomes.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
S.F. is Co-Lead of the Genes & Health programme, which is part-funded (including salary contributions) by a Life Sciences Consortium comprising Astra Zeneca PLC, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, GlaxoSmithKline Research and Development Limited, Maze Therapeutics Inc, Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc, Takeda Development Centre Americas Inc. For all other authors, no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures







References
-
- Cappellini MD, Fiorelli G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet. 2008;371:64–74. - PubMed
-
- Motulsky AG, Stamatoyannopoulos G. Clinical implications of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Ann Intern Med. 1966;65:1329–1334. - PubMed
-
- G6PD rapid diagnostic tests. 2025. [article online] Available from https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/case-management/diagn....
-
- Shenkutie TT, Nega D, Hailu A, Kepple D, Witherspoon L, Lo E, Negash MT, Adamu A, Gebremichael SG, Gidey B, Tasew G, et al. Prevalence of G6PD deficiency and distribution of its genetic variants among malaria-suspected patients visiting Metehara health centre, Eastern Ethiopia. Malar J. 2022;21:260. doi: 10.1186/s12936-022-04269-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

