Biallelic variants in BBOX1 cause L-Carnitine deficiency and elevated γ-butyrobetaine
- PMID: 41022783
- PMCID: PMC12480863
- DOI: 10.1038/s41525-025-00523-2
Biallelic variants in BBOX1 cause L-Carnitine deficiency and elevated γ-butyrobetaine
Abstract
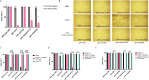
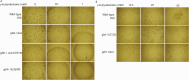
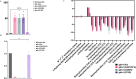
Gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase (BBOX1) catalyses the last step of carnitine biosynthesis, converting γ-butyrobetaine (γ-BB) into L-carnitine. Here we show, for the first time, that biallelic variants in BBOX1 are associated with decreased levels of L-carnitine and increased plasma levels of γ-BB in three patients from two unrelated families presenting with myopathic, neurodevelopmental, and late-onset psychiatric manifestations. Using a knockout C. elegans model of BBOX1 homolog, gbh-1, and strains harboring patient-derived variants (gbh-1(D72G) for p.Asp59Gly, gbh-1(G283R) for p.Gly263Arg, and gbh-1(G247Vfs6) for p.Gly227Valfs*6), we show very low L-carnitine levels and significantly elevated γ-BB in c.675delA and c.787G>A mutants, and moderately elevated γ-BB in c.176A>G. Furthermore, we observed a lethal embryonic phenotype for the gbh-1 loss-of-function strains, which was rescued upon L-carnitine supplementation. Our study provides novel insights into the clinical and biochemical consequences of BBOX1-related L-carnitine biosynthesis deficiency and establishes C. elegans as a model to study the effects of BBOX1 deficiency.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nezu, J. et al. Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is caused by mutations in a gene encoding sodium ion-dependent carnitine transporter. Nat. Genet.21, 91–94 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Rebouche, C. J. & Engel, A. G. Tissue distribution of carnitine biosynthetic enzymes in man. Biochim. Biophys. Acta630, 22–29 (1980). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

