Eosinophilic gastroduodenitis: a pediatric perspective
- PMID: 41024233
- PMCID: PMC12482670
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-025-02115-3
Eosinophilic gastroduodenitis: a pediatric perspective
Abstract
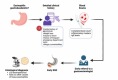
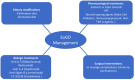
Eosinophilic gastroduodenitis (EoGD) is a group of chronic inflammatory disorders characterized by an increased presence of eosinophils in the stomach and duodenum. Although relatively rare, it is an increasingly recognized form of eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs) with significant clinical implications, particularly in pediatric patients. Despite advancements in diagnostic tools, considerable delays in diagnosis persist due to the nonspecific nature of clinical manifestations, which often resemble more common gastrointestinal disorders. Early referral to a gastroenterologist is critical, especially when patients present with persistent gastrointestinal signs and symptoms that do not improve with treatment for common conditions like irritable bowel syndrome. Food allergens and microbiota may play a role in the pathogenesis of this disease. Management typically involves a combination of dietary modifications, pharmacological treatments such as corticosteroids, and, in some cases, biologic agents targeting eosinophilic inflammation. However, long-term outcomes remain variable, and data on prognosis are still limited, underscoring the need for further research. Future studies should focus on validating new diagnostic markers and therapeutic strategies, better understanding long-term outcomes, and developing personalized treatment plans. A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating the expertise of gastroenterologists, allergists, dietitians, and surgeons, is crucial to ensure optimal patient care and management.
Keywords: Biologicals; Children; Eosinophilic gastroduodenitis; Food allergy; Non IgE-mediated food allergy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: Stefania Arasi has participated as an advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Novartis, DBV and Ferrero outside the submitted work. Mattia Giovannini reports personal fees from Sanofi.
Figures
References
-
- Licari A, Votto M, D’Auria E, Castagnoli R, Caimmi SME, Marseglia GL. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in children: a practical review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2020;16:106–14. 10.2174/1573396315666191022154432 - PubMed
-
- Gonsalves N. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;57:272–85. 10.1007/s12016-019-08732-1 - PubMed
-
- Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:335–58. 10.1177/2050640616689525 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulou A, Amil-Dias J, Auth MK, Chehade M, Collins MH, Gupta SK. at al. Joint ESPGHAN/NASPGHAN guidelines on childhood eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders beyond eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024;78:122–152. 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003877 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical