Phenotypic and epigenetic profiles of circulating NK cells in spontaneous HIV-1 controllers
- PMID: 41027310
- PMCID: PMC12513069
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105948
Phenotypic and epigenetic profiles of circulating NK cells in spontaneous HIV-1 controllers
Abstract
Background: NK cells play a key role in eliminating HIV-infected cells, but it is unclear whether there are specific NK cell receptor signatures in spontaneous HIV controllers.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of circulating NK cell phenotypes in people living with HIV (PLHIV), divided into spontaneous HIV controllers (HIC), normal progressors on antiretroviral therapy (non-HIC), and first-degree HIV-negative family members. Using supervised and unsupervised flow cytometry, we assessed NK cell markers and receptors. We performed an epigenetic analysis of H3K4me3 chromatin enrichment in NK cells from both HIC and non-HIC and measured IFNγ, Perforin and CD107a expression in NK cells upon stimulation with IL-2/IL-15, K562 cells, and IFNα. Additionally, we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping using data from HIC and non-HIC part of the 2000HIV study.
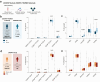
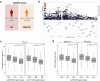
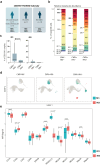
Findings: HIV controllers had higher levels of CD56bright NK cells and increased expression of NKp46, NKp30, and DNAM-1. The genetic association between protective MHC class I alleles and the NK cell receptor KIR2DL2/3 supports a genetic predisposition to HIV control. Unsupervised clustering identified an HIV-induced NK cell population, separate from CMV-induced NK cells. Epigenetic analysis revealed greater H3K4me3 marks in genes involved in immune response pathways, including IFNα, IL-15, and IL-2. The memory-like NK cell subpopulation was characterised by elevated expression of NKG2C and ILT2, with reduced KIR2DL2/3 in HIC. These memory NK cells were more responsive to stimulation with IFNα, resulting in increased production of IFNγ in HIC.
Interpretation: These results suggest that spontaneous HIV control is associated with an NK cell memory phenotype, shaped by HIV infection, epigenetic modifications, and genetic factors.
Funding: The authors are part of the 2000HIV study, which is supported by ViiV Healthcare.
Keywords: HIV; Innate immune memory; NK-cells; Normal progressors on ART; Spontaneous HIV-controllers.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests MGN is a scientific founder of TTxD, Biotrip, Lemba TX, and Salvina TX. LABJ is scientific founder of TTxD, Lemba TX, and Salvina TX. AH, NV, SDER, and JCS received a “New Investigators Scholarship” to attend the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2024 and 2025 to present data outside of the current manuscript. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Okulicz J.F., Lambotte O. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of elite controllers. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011;6:163–168. https://journals.lww.com/co-hivandaids/fulltext/2011/05000/epidemiology_... - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

