In Vivo DNA Assembly in Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 41027589
- PMCID: PMC12538579
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00296
In Vivo DNA Assembly in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
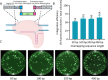
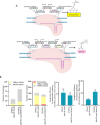
The oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica is an important platform organism for biotechnology applications. In this study, we established an in vivo DNA assembly system leveraging CRISPR-Cas9 for efficient genomic integration of multiple DNA fragments into the genome of Y. lipolytica. Using the green fluorescent protein mNeonGreen as a model, we demonstrated 53% correct assembly of three DNA fragments with homology arms as short as 50 bp. The system was further validated by constructing 2-3 step biosynthetic pathways for pigments betaxanthin and betanin. To improve the homologous recombination efficiency of Y. lipolytica, we expressed S. cerevisiae RAD52 (ScRAD52) or a Cas9-hBrex27 fusion protein. While ScRAD52 expression impaired growth, the cas9-hBrex27 fusion enhanced integration efficiency, particularly for multifragment pathway assemblies. The in vivo assembly method simplifies pathway construction and gene overexpression in Y. lipolytica.
Keywords: Yarrowia lipolytica; homologous recombination; in vivo DNA assembly; pathway construction.
Figures
References
-
- Holkenbrink C., Ding B.-J., Wang H.-L., Dam M. I., Petkevicius K., Kildegaard K. R., Wenning L., Sinkwitz C., Lorántfy B., Koutsoumpeli E.. Production of moth sex pheromones for pest control by yeast fermentation. Metabolic Engineering. 2020;62:312–321. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2020.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

