Calibration of multisite raters for prospective visual reads of amyloid PET scans
- PMID: 41030129
- PMCID: PMC12484700
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70732
Calibration of multisite raters for prospective visual reads of amyloid PET scans
Abstract
Introduction: In multicenter Alzheimer's disease studies, amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) visual reads are typically performed centrally by a few experts. Incorporating a broader reader network enhances scalability and generalizability.
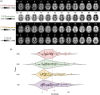
Methods: Ten neuroimaging experts from eight Alzheimer's Disease Research Centers (ADRCs) visually read 180 amyloid PET scans (30 scans and 15 duplicate scans for each of four tracers, imaged across a wide variety of scanners), using preferred reading software without anatomical imaging or quantitation. Scans were classified as elevated or non-elevated per tracer-specific criteria. Inter- and intra-rater agreement was assessed.
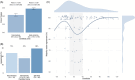
Results: Inter-rater agreement was substantial (Fleiss' κ = 0.78), with full consensus on 69% of scans. Inter-rater reliability was substantial to perfect across tracers (Fleiss' κ = 0.70-0.87). Intra-rater agreement was substantial to perfect (Cohen's κ = 0.79-1). Scans with intermediate (10-40 Centiloid) quantitation had lower reader agreement.
Discussion: A multicenter expert network achieved substantial agreement classifying amyloid PET scans. These scans provide a standard for reader training and reliability assurance in future studies.
Highlights: Calibration methods ensure reliable amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) visual reads across multiple raters. Substantial agreement is possible across readers using their preferred tools. Agreement is also substantial regardless of the amyloid PET tracer used. Scans with intermediate (10-40 Centiloid) quantitation have lower reader agreement. The calibration set will become a training tool for amyloid PET visual read studies.
Keywords: Amyloid positron emission tomography; inter‐rater reliability; intra‐rater reliability; visual reader calibration; visual reads.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
D.N.S.M. receives research support from NIH and serves on an Alzheimer's Association research council. R.L.J. has served as a paid consultant for GE Healthcare. D.R.J. has served as a consultant and/or on advisory boards for Novartis, Telix, and Cellectar. M.E.K. receives research support from NIH and Alzheimer's Association. J.E.M. receives research support from NIH, Eli Lilly/Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, GE Healthcare, Novartis, and Cytosite Biopharma. He has served as a consultant to Eli Lilly/AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, GE Healthcare, Telix, and Novartis, and he also received honoraria from Telix. I.M.N. receives research support from NIH. He has served as a consultant to Subtle Medical and on an advisory board for Eisai. V.L.V. receives research support from NIH and Aging Mind Foundation. He has been a consultant or paid speaker at sponsored conference sessions for Eli Lilly, Life Molecular Imaging, ACE Barcelona, IXICO, and AC Immune. M.R.P has served as a paid scientific consultant for Avid Radiopharmaceuticals and Lantheus Medical Imaging and as a paid speaker for PETNET Solutions. She is the board chair of the American Board of Nuclear Medicine (ABNM). C.C.W. receives research support from the NIH and Alzheimer's Association. He has previously received honoraria from LCN, Onviv, Kinetix Group, and the American Academy of Neurology. W.A.K. receives research support from the NIH. He serves on external advisory committees for several ADRCs, including Kansas University, Boston University, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. He is an Associate Editor for
Figures

References
-
- Rabinovici GD, Gatsonis C, Apgar C, Chaudhary K, Gareen I, Hanna L, et al. Association of amyloid positron emission tomography with subsequent change in clinical management among medicare beneficiaries with mild cognitive impairment or dementia. JAMA. 2019;321:1286‐1294. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

