Spatial-hindrance-based pro-Adalimumab prevents anti-idiotypic antibody interference in pharmacokinetic and therapeutic efficacy
- PMID: 41030274
- PMCID: PMC12478331
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.70015
Spatial-hindrance-based pro-Adalimumab prevents anti-idiotypic antibody interference in pharmacokinetic and therapeutic efficacy
Abstract
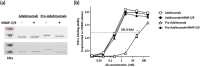
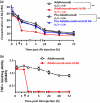
Adalimumab (Humira) represents a major advance in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy. However, with long-term administration of Adalimumab, anti-idiotypic antibody (anti-Id Ab) accelerates the Adalimumab clearance rate and reduces the therapeutic effect. To avoid the interference of anti-Id Ab, we used an autologous hinge region as a spatial-hindrance-based Ab lock and connected it to the N-terminal of the light chain and heavy chain via substrate peptides (MMP-2/9) to cover the CDR binding site of Adalimumab to generate pro-Adalimumab. The Ab lock masks the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of Adalimumab, thus avoiding interference from anti-Id Ab. Pro-Adalimumab demonstrated a 241.6 times weaker binding ability to TNFɑ than Adalimumab. In addition, pro-Adalimumab showed a 46.6-fold greater blocking of anti-Adalimumab Id Ab in comparison to Adalimumab prior to activation. Similar results were observed with other clinical antibodies, such as pro-Infliximab (anti-TNFɑ Ab) and pro-Nivolumab (anti-PD-1). Furthermore, pro-Adalimumab maintained consistent pharmacokinetics regardless of the presence of anti-Adalimumab Id antibodies, while Adalimumab showed a 49% clearance increase, resulting in a near complete loss of function. Additionally, pro-Adalimumab was able to avoid neutralization and efficiently reduce RA progression in the presence of anti-Adalimumab Id Ab in vivo. In summary, we developed a pro-Adalimumab that avoids interference from anti-Id Abs, thereby addressing the biggest issue limiting clinical efficacy. The findings enclosed herein may have potentially broad application in antibody therapies.
Keywords: Ab lock (hinge); avoid interference from anti‐id Abs; protease activation; pro‐adalimumab; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chan AC, Carter PJ. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(5):301‐316. - PubMed
-
- Güler‐Yüksel M, Allaart CF, Watt I, et al. Treatment with TNF‐α inhibitor infliximab might reduce hand osteoarthritis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(10):1256‐1262. - PubMed
-
- Bacquet‐Deschryver H, Jouen F, Quillard M, et al. Impact of three anti‐TNFalpha biologics on existing and emergent autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis and spondylarthropathy patients. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28(5):445‐455. - PubMed
-
- Casadevall A, Dadachova E, Pirofski L‐a. Passive antibody therapy for infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2(9):695‐703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

