Dietary Potassium Synergistically Enhances Anti-Obesity Efficacy of Garcinia Cambogia Complex in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
- PMID: 41034179
- PMCID: PMC12580639
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2025.069
Dietary Potassium Synergistically Enhances Anti-Obesity Efficacy of Garcinia Cambogia Complex in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
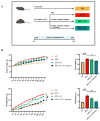
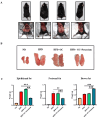
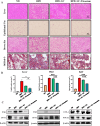
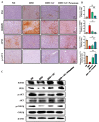
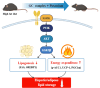
Obesity is a global health problem associated with several metabolic disorders. Conventional dietary supplements such as Garcinia cambogia, catechin, and conjugated linoleic acid (GC complex) are widely used for weight loss but raise concerns about long-term efficacy and safety. Recent advances in nutritional research suggest that combining dietary mineral elements might enhance obesity therapeutic outcomes. The objective of this study is to investigate the potential synergistic effects of potassium in combination with GC complex in a mouse model of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity. When administered daily orally for 12 weeks, the HFD+GC+Potassium group exhibited synergistically reduced adipocyte size in both white and brown adipose tissue compared to the HFD group, indicating a reduction in fat storage. In addition, HFD+GC+Potassium group exhibited a marked improvement in metabolic profiles, characterized by reduced fasting glucose and total cholesterol levels without toxicity, compared with HFD group. Histological analyses confirmed the effectiveness of the treatment, showing marked reductions in hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation, as evidenced by H&E and Oil Red-O staining in the HFD+GC+Potassium group. Significantly, the study showed that potassium supplementation in combination with GC complex improved lipid metabolism and energy expenditure by increasing the expression of phosphorylated acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (p-ACC1) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1), while decreasing the levels of fatty acid synthase (FAS) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) through IGF1R/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β axis. These findings suggest that the combination of GC complex and dietary potassium may offer a synergistic effect and a safe strategy for managing obesity by reducing fat accumulation and enhancing metabolic health.
Keywords: High fat; Lipid metabolism; Obesity; Potassium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Askari M., Mozaffari H., Jafari A., Ghanbari M., Darooghegi Mofrad M. The effects of magnesium supplementation on obesity measures in adults: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021;61:2921–2937. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1790498. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

