Polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes shows context-dependent effects across populations
- PMID: 41034193
- PMCID: PMC12488948
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63546-4
Polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes shows context-dependent effects across populations
Abstract
Polygenic risk scores hold prognostic value for identifying individuals at higher risk of type 2 diabetes. However, further characterization is needed to understand the generalizability of type 2 diabetes polygenic risk scores in diverse populations across various contexts. We systematically characterize a multi-ancestry type 2 diabetes polygenic risk score among 244,637 cases and 637,891 controls across diverse populations from the Population Architecture Genomics and Epidemiology Study and 13 additional biobanks and cohorts. Polygenic risk score performance is context dependent, with better performance in those who are younger, male, without hypertension, and not obese or overweight. Additionally, the polygenic risk score is associated with various diabetes-related cardiometabolic traits and type 2 diabetes complications, suggesting its utility for stratifying risk of complications and identifying shared genetic architecture between type 2 diabetes and other diseases. These findings highlight the need to account for context when evaluating polygenic risk score as a tool for type 2 diabetes risk prognostication and the potentially generalizable associations of type 2 diabetes polygenic risk score with diabetes-related traits, despite differential performance in type 2 diabetes prediction across diverse populations. Our study provides a comprehensive resource to characterize a type 2 diabetes polygenic risk score.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: R.J.F.L. has acted as a member of advisory boards and as a speaker for Ely Lilly and the Novo Nordisk Foundation, for which she has received fees. L.M.R. is a consultant for the NHLBI TOPMed Administrative Coordinating Center (through Westat). U.P. was a consultant with AbbVie, and her husband holds individual stocks for the following companies: BioNTech SE—ADR, Amazon, CureVac BV, Google/Alphabet Inc Class C, NVIDIA Corp, Microsoft Corp. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
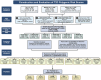
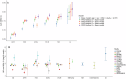
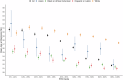
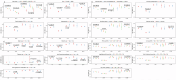

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Atlas 2021 10th edn (International Diabetes Federation, 2021).
-
- Bommer, C. et al. Global economic burden of diabetes in adults: projections from 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care41, 963–970 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03CA287235/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01DK123019/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL142302/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NNF20OC0059313/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- R01 DK123019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL174378/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- NPRP11S-0114-180299/Qatar National Research Fund (QNRF)
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA287235/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL143885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL163262/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01DK139598/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01HL156991/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HD030880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL163262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL143885/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- PPM2-0226-170020/Qatar National Research Fund (QNRF)
- P50 CA097186/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA261339/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U54HG013243/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R00CA246063/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 CA261339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA097186/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- U54 HG013243/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL151152/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL151152/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL142302/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 DK139598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK122503/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL156991/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124097/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NNF18CC0034900/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- R01 HL174378/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA246063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1DK078616/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30CA015704/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 DK122503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD30880/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

