Quality controlled, reliable groundwater level data with corresponding specific yield over India
- PMID: 41034238
- PMCID: PMC12489037
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05899-5
Quality controlled, reliable groundwater level data with corresponding specific yield over India
Abstract
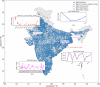
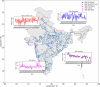
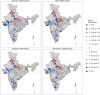
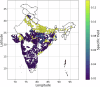
Groundwater is a vital resource for domestic, agricultural, and industrial use, with its demand growing due to population growth and climate change. Several studies have identified groundwater depleting in India at unsustainable rate over North-west part, but a contrasting trend is observed in the southern India. To better study groundwater dynamics quality-controlled and reliable well data is essential, which is missing. Here we process seasonal groundwater levels from 32,299 wells across India to obtain reliable well data and provide respective specific yields. Initially, wells with no data and negative values are removed. Later three-sigma method is imposed on each well to eliminate outliers. Finally, wells with at least two values per year, with no value repeating more than twice consecutively, are retained, resulting in 2,759 reliable wells. We used vectorization-based method to classify aquifer types and estimated specific yields based on hydrogeological map. We also provide open access to data and scripts so that researchers can study groundwater variations, compare GRACE and model-based groundwater estimates against in-situ well data.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Baldwin, H. L. & McGuinness, C. L. A primer on ground water. (United States Department of the Interior, Geological Survey, 1963).
-
- WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme). The United Nations world water development report 2015: Water for a sustainable world. UNESCO Retrieved from https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000231823_eng (2015).
-
- Zektser, I. S. & Everett, L. G. Groundwater resources of the world and their use (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, 2004).
-
- Döll, P. Vulnerability to the impact of climate change on renewable groundwater resources: A global-scale assessment. Environ. Res. Lett.4(3), 035006 (2009).
-
- Famiglietti, J. S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Change.4(11), 945–948 (2014).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

