Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of Aripiprazole once-monthly, long-acting intramuscular injection for Chinese adults with schizophrenia
- PMID: 41034820
- PMCID: PMC12487114
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-025-07407-w
Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of Aripiprazole once-monthly, long-acting intramuscular injection for Chinese adults with schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Aripiprazole once-monthly (AOM), a long-acting injectable antipsychotic, is increasingly used in managing schizophrenia. However, to date, there has been no disclosure of pharmacokinetic data for AOM long-acting injection in the Chinese population. The present study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of AOM of Chinese patients with schizophrenia.
Methods: The single-administration part of the study was single-center and multiple-dose, in which 300/400-mg AOM was administered to 24 patients with schizophrenia. In the multiple-administration part of the study, 400-mg of AOM was administered once every 4 weeks for 20 consecutive weeks to 12 subjects. Pharmacokinetic parameters (e.g., e.g., Cmax, tmax, AUC0-∞, t1/2, and CL/F) were derived via non-compartmental analysis using actual sampling times, with bootstrap-derived confidence intervals for non-normal data. Safety evaluation included monitoring of adverse events (AEs), physical examinations, vital signs, and clinical laboratory tests.
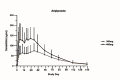
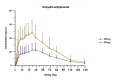
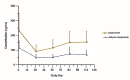
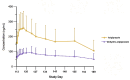
Results: Following single administration of AOM (300-mg or 400-mg), maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) values of aripiprazole were 85.05 ± 42.11 and 175.25 ± 67.84 ng/mL, respectively; median times to achieve Cmax (tmax) were 816.17 and 588.84 h, respectively; and elimination half-life (t1/2) values were 647.18 ± 234.59 and 547.17 ± 258.48 h, respectively. Following multiple administration of AOM, the Cmax of aripiprazole was 270.18 ± 113.37 ng/mL, the median tmax was118.83, and the t1/2 was 1138.78 ± 998.77 h. In vivo exposure to aripiprazole increased with the AOM dose. No severe AEs were observed in single- or multiple-administration studies.
Conclusions: The pharmacokinetics of AOM support its clinical use as a 4-week injectable regimen, with favorable tolerability and safety profiles observed in Chinese patients with schizophrenia.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: Single-administration NCT03287505 first submitted on 15 May 2017, Multiple-administration NCT03285503 first submitted on 11 Sep 2017.
Keywords: Aripiprazole; Aripiprazole once-monthly (AOM); Long-acting intramuscular injection; Pharmacokinetics; Safety; Schizophrenia; Tolerability.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethics committee of The Beijing Anding Hospital Ethics. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from individual participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Almond S, Knapp M, Francois C, Toumi M, Brugha T. Relapse in schizophrenia: costs, clinical outcomes and quality of life. Br J Psychiatry. 2004;184:346–51. - PubMed
-
- ssociation AP, editor. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: Washington, DC, 2021.
-
- Kane JM. Review of treatments that can ameliorate nonadherence in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(Suppl 5):9–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

