CircSPINT2 confers sensitivity to osimertinib via hsa-miR-1296-3p/RBP1 axis and inhibits NSCLC progression
- PMID: 41035422
- PMCID: PMC12481618
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omton.2025.201007
CircSPINT2 confers sensitivity to osimertinib via hsa-miR-1296-3p/RBP1 axis and inhibits NSCLC progression
Abstract
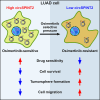
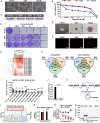
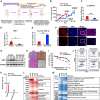
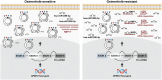
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common type of lung cancer. Prolonged treatment of LUAD with 1st/2nd generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) promotes the emergence of secondary EGFR T790M mutation conferring resistance to these drugs. Patients who acquire EGFR T790M mutation respond to the 3rd generation EGFR-TKI osimertinib but develop resistance within 12 months. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are notably associated with cancerogenesis, making them promising biomarkers or therapeutic targets. In this study, we aimed to identify circRNAs that regulate osimertinib resistance and elucidate the functions and mechanisms to reveal potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers for osimertinib-resistant LUAD. The analysis of circRNA transcriptome sequencing identified circSPINT2 to be downregulated in osimertinib-resistant cell lines. The loss-/gain-of-function assays revealed that circSPINT2 sensitizes cells to osimertinib treatment by inducing apoptosis. Functionally, circSPINT2 enhanced the expression of RBP1 by sponging hsa-miR-1296-3p. Osimertinib-resistant xenograft tumor model was established by long-term osimertinib treatment, and the molecular and histologic analysis of subcutaneous xenograft tumors corroborated our in vitro findings. Conclusively, our study demonstrates that circSPINT2 possesses tumor-suppressive functions; the restoration of circSPINT2 expression level confers sensitivity to osimertinib treatment via miR-1296-3p/RBP1 axis. The secreted circSPINT2 may serve as a monitoring biomarker for osimertinib resistance status in LUAD.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; L858R; NSCLC; T790M; biomarker; circular RNA; lung cancer; non-coding RNA; osimertinib; osimertinib-resistant.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Yoshimura A., Yamada T., Okura N., Takeda T., Hirose K., Kubota Y., Shiotsu S., Hiranuma O., Chihara Y., Tamiya N., et al. Clinical characteristics of osimertinib responder in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR-T790M mutation. Cancers. 2019;11:365. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumari N., Singh S., Haloi D., Mishra S.K., Krishnani N., Nath A., Neyaz Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation frequency in squamous cell carcinoma and its diagnostic performance in cytological samples: a molecular and immunohistochemical study. World J. Oncol. 2019;10:142–150. doi: 10.14740/wjon1204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
