Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity and pharmacodynamics of 9MW1911, an anti-ST2 monoclonal antibody: results from a first-in-human phase 1 study
- PMID: 41035917
- PMCID: PMC12481716
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1647816
Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity and pharmacodynamics of 9MW1911, an anti-ST2 monoclonal antibody: results from a first-in-human phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: 9MW1911 is a high-affinity human IgG4 monoclonal antibody targeting ST2, the human IL-33 receptor. It may have anti-inflammatory effects by blocking the IL-33/ST2 pathway. This first-in-human trial (NCT05803902) aimed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity and pharmacodynamics of 9MW1911 in healthy participants.
Methods: This phase I, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study enrolled 48 healthy adults. After a screening period of up to 28 days, they received a single ascending intravenous dose (ranging from 25 to 1200 mg) of 9MW1911 (n = 6 per dose) or matched placebo (n = 2 per dose). Parameters of safety, pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity and pharmacodynamics were evaluated, with follow-up visits until day 113 post-dosing.
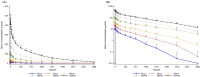
Results: 9MW1911 was safe and well-tolerated across various doses. Most AEs were of mild to moderate, resolved without treatments. No dose-related AEs were observed, and the only serious AE (fetal malformation) was deemed unrelated to the study drug. No deaths or discontinuations due to AEs occurred. 9MW1911 ranging from 25 mg to 1,200 mg demonstrated a non-linear increase in exposure, while a linear PK profile was observed in the dose range from 100 mg to 1200 mg. No anti-drug antibodies were detected in any participants. Total sST2 in serum increased and stabilized at higher dose levels, demonstrating sustained target binding.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates that 9MW1911 was safe and well-tolerated in healthy participants. As 9MW1911 concentrations increased,the sustained elevation of sST2 in the higher dose levels (100mg-1200 mg) suggested that the target-mediated drug disposition (TMDD) elimination became saturated, leading to the observed linear PK profile. These data support the continued development of 9MW1911 for the therapeutic use in the relevant disease.
Keywords: 9MW1911; ST2; first-in-human trial; pharmacokinetics; safety.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Li, Wang, Li, Zhao, Wu, Fu, Yin, Feng, Hu, Guo and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
Author(s) DY, JF, ZH and YG were employed by Mabwell (Shanghai) Bioscience Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from Mabwell (Shanghai) Bioscience Co., Ltd. The funder had the following involvement in the study: study design, conduct, data collection, management, analysis, and interpretation.
Figures


References
-
- Bergers G., Reikerstorfer A., Braselmann S., Graninger P., Busslinger M. (1994). Alternative promoter usage of the Fos-responsive gene Fit-1 generates mRNA isoforms coding for either secreted or membrane-bound proteins related to the IL-1 receptor. EMBO J. 13 (5), 1176–1188. 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06367.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

