Effect of cobalt ions on TNF-α and IL-6 secretion by fibroblasts surrounding hip periprosthetic membrane
- PMID: 41036386
- PMCID: PMC12479478
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1651049
Effect of cobalt ions on TNF-α and IL-6 secretion by fibroblasts surrounding hip periprosthetic membrane
Abstract
Aims: The periprosthetic fibroblast-like cells (PPFs) play an important role in aseptic loosening after total hip arthroplasty (THA). However, little is known about fibroblast metabolism in aseptic loosening. Proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and il-6 interleukin-6 (IL-6) are involved in periprosthetic osteolysis. Cobalt (Co) ions are capable of inducing cytokines from macrophage. In this study, we investigated the effects of Co2+ on glycolysis and secretion of TNF-α and IL-6 in PPFs.
Materials and methods: Fibroblasts were isolated from synovial tissues of osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, as well as from the periprosthetic pseudomembrane of patients undergoing revision surgery for aseptic loosening. Cells were cultured with or without Co2+. Following treatment, fibroblast viability was assessed using the MTT assay. To evaluate glycolysis, glucose uptake and lactate secretion were measured using specific assay kits. Furthermore, gene expression of key glycolysis enzymes (glucose transporter -1(GLUT1), hexokinase-2(HK2)) was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR), while protein expression of protein kinase B (AKT) and phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) was detected via Western blotting. Finally, TNF-α and IL-6 secretion into the culture supernatant was quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits.
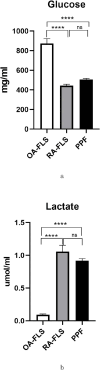
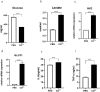
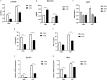
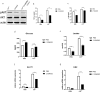
Results: Increased glucose uptake and lactic acid secretion occurred in PPFs. Exposure to Co2+ significantly increased glucose uptake, lactate secretion, GLUT1/HK2 mRNA expression, and TNF-α/IL-6 levels in PPFs. This Co2+-induced enhancement of glycolysis and cytokine secretion was dependent on glycolytic activity, as inhibition with 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) reduced all measured parameters. Furthermore, Co2+ stimulation increased pAKT protein expression in PPFs, indicating activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Consistent with this, treatment with the phosphatidylinositol three kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) inhibitor LY294002 attenuated the Co2+-induced increases in glucose uptake, lactate secretion, GLUT1/HK2 mRNA, and TNF-α/IL-6 levels.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that Co2+ enhances TNF-α and IL-6 secretion in PPFs by upregulating glycolysis. This glycolytic regulation of cytokine production appears to be mediated by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, identifying it as a potential novel therapeutic target for preventing aseptic loosening.
Keywords: Co2+; aseptic loosening; fibroblast; glycolysis; proinflammatory cytokines.
Copyright © 2025 Cai, Li and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer XY declared a shared parent affiliation with the author(s) to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

