Influence of right ventricular pacing on mitochondrial function in adults
- PMID: 41036599
- PMCID: PMC12489464
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70568
Influence of right ventricular pacing on mitochondrial function in adults
Abstract
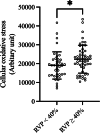
Right ventricular pacing (RVP) frequency and duration significantly associate with RVP-induced cardiomyopathy. However, human data regarding RVP burden and mitochondrial function is scarce. We aimed to investigate the association between the duration and percentage of RVP and mitochondrial function in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). This cross-sectional study enrolled individuals with a permanent pacemaker device with RVP capabilities, implanted for over 1 month, and exhibiting preserved left ventricular (LV) systolic function. The assessment of mitochondrial function was conducted using PBMCs to explore its correlation with RVP burden since pacemaker implantation. The analysis included 96 patients. The majority of patients had advanced or third-degree atrioventricular block, with a median RVP percentage of 84% and a median duration since implantation was 64 months. Substantial RVP percentage (RVP ≥ 40%) was independently associated with increased cellular oxidative stress (p = 0.015). Patients with longer RVP exposure (duration since implantation ≥ 60 months) were independently associated with increased mitochondrial oxidative stress (p = 0.030). Both associations remained significant after adjusting for confounding variables. In individuals with permanent pacemaker and preserved LV systolic function, substantial RVP percentage and prolonged RVP exposure were independently associated with increased cellular and mitochondrial oxidative stress.
Keywords: mitochondrial function; oxidative stress; permanent pacemaker; right ventricular pacing.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agnetti, G. , Kaludercic, N. , Kane, L. A. , Elliott, S. T. , Guo, Y. , Chakir, K. , Samantapudi, D. , Paolocci, N. , Tomaselli, G. F. , & Kass, D. A. (2010). Modulation of mitochondrial proteome and improved mitochondrial function by biventricular pacing of dyssynchronous failing hearts. Circulation. Cardiovascular Genetics, 3, 78–87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betsou, F. , Gaignaux, A. , Ammerlaan, W. , Norris, P. J. , & Stone, M. (2019). Biospecimen science of blood for peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) functional applications. Current Pathobiology Reports, 7, 17–27.
-
- Bongiorni, M. G. , Proclemer, A. , Dobreanu, D. , Marinskis, G. , Pison, L. , Blomstrom‐Lundqvist, C. , Scientific Initiative Committee, European Heart Rhythm Association , Blomström‐Lundqvist, C. , Bongiorni, M. G. , & Chen, J. (2013). Preferred tools and techniques for implantation of cardiac electronic devices in Europe: Results of the European Heart Rhythm Association survey. Europace, 15, 1664–1668. - PubMed
-
- Calle, S. , Duchenne, J. , Puvrez, A. , De Pooter, J. , Voigt, J. , & Timmermans, F. (2021). Strain‐based staging classification of left bundle branch block‐induced cardiac remodeling predicts reverse remodeling after cardiac resynchronization therapy. European Heart Journal, 42, ehab724‐016.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

