Direct and efficient synthesis of nucleosides through the ortho-(tert-butylethynyl)phenyl thioglycosides (BEPTs) protocol
- PMID: 41038824
- PMCID: PMC12491467
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63874-5
Direct and efficient synthesis of nucleosides through the ortho-(tert-butylethynyl)phenyl thioglycosides (BEPTs) protocol
Abstract
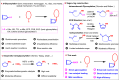
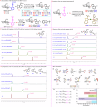
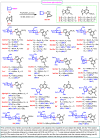
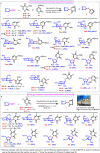
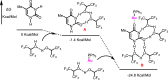
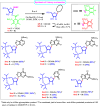
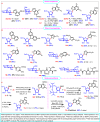
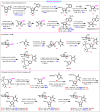
Nucleosides are highly biologically relevant compounds, and are widely clinically used as drugs for the treatment of virus/bacteria infections and cancers. However, efficient chemical synthesis of nucleoside is highly difficult due to the low reactivity of nucleobases acceptors, challenging the existing synthetic protocols. Here we show an alternative synthetic protocol with judiciously designed o-(tert-butylethynyl)phenyl thioglycosides (BEPTs) as donors. The protocol is featured by stable glycosylation donors and high efficiency, direct glycosylation without the need for preactivation/silylation of nucleobases, broad substrate scope, capacity in furnishing 2-deoxy-nucleosides, cost efficiency, scalability, and significantly improved reaction speed, and exhibits favorable and profound solvent effects for hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP). To check the practicality of the protocol, efficient preparation of angustmycin A and dJ is accomplished. The reaction mechanisms are systematically investigated, providing deep insights to the BEPT protocol.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Uhlmann, E. & Peyman, A. Antisense oligonucleotides: a new therapeutic principle. Chem. Rev.90, 543–584 (1990).
-
- Gaynor, J. W., Campbell, B. J. & Cosstick, R. RNA interference: a chemist’s perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev.39, 4169–4184 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Jordheim, L. P., Durantel, D., Zoulim, F. & Dumontet, C. Advances in the development of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues for cancer and viral diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.12, 447–464 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

