ABCC4 impairs the clearance of plasma LDL cholesterol through suppressing LDLR expression in the liver
- PMID: 41038958
- PMCID: PMC12491593
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08818-x
ABCC4 impairs the clearance of plasma LDL cholesterol through suppressing LDLR expression in the liver
Abstract
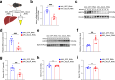
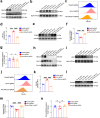
Low expression level of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) in hepatocytes leads to hypercholesterolemia and eventually contributes to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Here, we report that inhibition of hepatocyte ABCC4, identified as a top hit from large-scale CRISPR/Cas9 screens, significantly increases hepatic LDLR abundance and enhances LDL cholesterol clearance. As a hepatic transporter for cAMP efflux, ABCC4 silencing alters its intracellular distribution and activates the downstream Epac2/Rap1a signaling pathway, which ultimately blocks PCSK9 protein expression, thereby preventing lysosomal degradation of LDLR. Furthermore, in both male mice and cell models, we demonstrate that liver-specific disruption and pharmacological inhibition of ABCC4 elevate hepatic plasma membrane LDLR levels and reduce plasma LDL cholesterol through ABCC4-cAMP-PCSK9 pathway. Collectively, our genome-wide CRISPR screening offers a valuable resource for identifying LDLR modifiers, providing potential insights for therapeutic strategies in hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lorkowski, S. & Cullen, P. Atherosclerosis: pathogenesis, clinical features and treatment. Encycl. Life Sci.10, 1–11 (2007).
-
- Helkin, A. et al. Dyslipidemia part 1-review of lipid metabolism and vascular cell physiology. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg.50, 107–118 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Alfarisi, H. A. H., Mohamed, Z. B. H. & Ibrahim, M. B. Basic pathogenic mechanisms of atherosclerosis. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci.7, 116–125 (2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

