Normothermic machine perfusion converges transplant induced transcript profiles in low and high risk DBD and DCD livers
- PMID: 41039014
- PMCID: PMC12491471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17448-6
Normothermic machine perfusion converges transplant induced transcript profiles in low and high risk DBD and DCD livers
Abstract
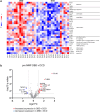
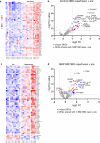
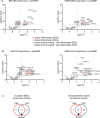
Normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) of donated livers is emerging as a superior preservation technology versus static cold storage (SCS) for transplant, transforming a metabolically dormant organ to a functioning state that improves outcomes of marginal liver transplants. Mechanisms underlying improved NMP restoration of donation after brain death (DBD) and donation after circulatory death (DCD) livers remain incompletely defined. We tested the hypothesis that NMP would decrease transcripts encoding inflammatory mediators following both perfusion and transplant of DBD and DCD livers. Biopsy transcript expression profiles were determined from SCS DBD livers at pre-SCS preservation and transplant reperfusion and from benchmark and outside benchmark criteria DBD and DCD livers pre-NMP, after 6-7 h of NMP, and after transplant reperfusion. Compared to SCS livers, NMP programs converged transcript profiles of DCD and DBD livers, decreasing transplant reperfusion-induced inflammatory transcripts while increasing transcripts promoting wound healing and tissue repair processes, but did not obviate the high occurrence of adverse events in the outside benchmark DCD livers transplants.
Keywords: Gene expression; Graft preservation; Inflammation; Ischemia-reperfusion injury; Liver transplantation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wolfe, R. A., Merion, R. M., Roys, E. C. & Port, F. K. Trends in organ donation and transplantation in the united states, 1998–2007. Am. J. Transpl.9, 869–878 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Rana, R. et al. Predicting liver allograft discard: the discard risk index. Transplantation102, 1520–1529 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Malik, T. et al. Pediatric discard risk index for predicting pediatric liver allograft discard. Pediatr. Transpl.e1396310.1111/petr.13963 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

