4-1BB+ Tregs and inhibitory progenitor exhausted T cells confer resistance to anti-PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4 combination therapy
- PMID: 41045934
- PMCID: PMC12629806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102408
4-1BB+ Tregs and inhibitory progenitor exhausted T cells confer resistance to anti-PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4 combination therapy
Abstract
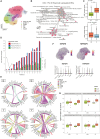
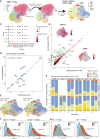
Predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in cancer remain elusive. From a previous phase 2 neoadjuvant immunotherapy window-of-opportunity study, we present the single-cell RNA and T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing analysis of 57 pre- and post-treatment tumor biopsies from head and neck cancer patients treated with durvalumab (anti-PD-L1) alone or with tremelimumab (anti-CTLA-4), identifying key cellular and molecular predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) response. Malignant cells and neutrophil senescence promote ICI response. While CXCL13+ exhausted T (Tex) cells enhance response through 4-1BB signaling, anti-CTLA-4 induces 4-1BB+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) restricting ICI efficacy. These opposing roles of 4-1BB in different cellular contexts may explain the limited benefit of combinatorial immunotherapy observed in clinical trials. We identify two subsets of tumor-reactive progenitor Tex (Tpex): ICI-responsive Tpex1 and ICI-resistant Tpex2, a subset characterized by KLRB1 and IL17R. The balance of Tpex1 and Tpex2 associates with ICI response across multiple cancers, offering insights into sustaining response. This study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03737968).
Keywords: dual ICB; durvalumab; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immunotherapy; progenitor exhausted T; single-cell RNA; single-cell TCR; tremelimumab.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Cohen E.E.W., Soulières D., Le Tourneau C., Dinis J., Licitra L., Ahn M.J., Soria A., Machiels J.P., Mach N., Mehra R., et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;393:156–167. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31999-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

