Development of polymyxin- and aminoglycoside-based outer membrane permeabilizers: a review
- PMID: 41048486
- PMCID: PMC12488743
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1625300
Development of polymyxin- and aminoglycoside-based outer membrane permeabilizers: a review
Abstract
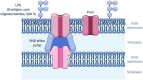
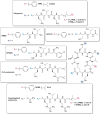
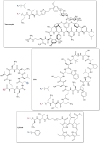
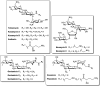
The prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) necessitates the development of alternative therapeutic options, particularly against critical priority Gram-negative pathogens. The utilization of antibiotic adjuvants or potentiators is an advantageous strategy that targets bacterial resistance mechanisms, thereby augmenting the activity of an antibiotic used in combination. Among these, outer membrane (OM) permeabilizers are a promising class of adjuvants which compromise the OM barrier unique to Gram-negative bacteria. This review focuses on the emerging role of polymyxins and aminoglycosides - two structurally distinct antibiotics with different modes of action, but share the ability to interact with the bacterial OM. Here, we explore the design, modification, and application of polymyxin- and aminoglycoside-based OM permeabilizers, highlighting their potential against resistant Gram-negative infections.
Keywords: aminoglycosides; antibiotic adjuvants; combination therapy; outer membrane permeabilizers; polymyxins; potentiators.
Copyright © 2025 Ramirez and Schweizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
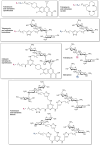
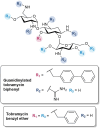
References
-
- Abdul Rahim N., Zhu Y., Cheah S.-E., Johnson M. D., Yu H. H., Sidjabat H. E., et al. (2021). Synergy of the polymyxin-chloramphenicol combination against New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae is predominately driven by chloramphenicol. ACS Infect. Dis. 7, 1584–1595. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00661, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

