Noninvasive Computed Tomography-Based Quantification of Tumor Fibrosis Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Response to Gemcitabine/Nab-Paclitaxel
- PMID: 41049608
- PMCID: PMC12491862
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0937
Noninvasive Computed Tomography-Based Quantification of Tumor Fibrosis Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Response to Gemcitabine/Nab-Paclitaxel
Abstract
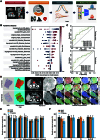
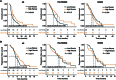
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) carries a dismal prognosis. Chemotherapy remains the mainstay for unresectable cases, yet regimens like AG (gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel) exhibit heterogeneous efficacy. Tumor fibrosis has emerged as a potential predictor of treatment response but lacks validated noninvasive assessment methods. To address this, in this multicenter study, tumor fibrosis was quantified in 361 patients with resectable PDAC from SYSUCC, XYCSU, and TCGA cohorts using deep learning-based tissue segmentation on hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole-slide images. Fibrosis was defined as stromal proportion, and its association with overall survival (OS) was evaluated. Transcriptomic profiling was performed in 51 XYCSU cases to validate the biological relevance of fibrosis quantification. A radiomics model (RM) was then developed using preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scans from SYSUCC to predict fibrosis and externally validated in XYCSU. Clinical utility was assessed in an independent cohort of 295 unresectable PDAC patients treated with AG, FOLFIRINOX, or SOXIRI. High fibrosis correlated with prolonged OS across resectable cohorts (all P < 0.05). Transcriptomic analysis revealed enrichment of fibrosis-related pathways in high-fibrosis tumors. The RM achieved an area under the curve of 0.718 (95% confidence interval: 0.627 to 0.823) in the external test set. Among patients receiving AG, those with CT-predicted high fibrosis had significantly longer progression-free survival (median: 6.23 versus 4.70 months, P = 0.037) and OS (13.37 versus 7.73 months, P = 0.002). No significant survival benefit was observed for high-fibrosis patients receiving FOLFIRINOX or SOXIRI. CT-based fibrosis quantification offers a robust, noninvasive biomarker for predicting AG efficacy in unresectable PDAC.
Copyright © 2025 Qiuxia Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Gyawali B, Booth CM. Treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer: 25 years of innovation with little progress for patients. Lancet Oncol. 2024;25(2):167–170. - PubMed
-
- Hu ZI, O’Reilly EM. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21(1):7–24. - PubMed
-
- Mastrantoni L, Chiaravalli M, Spring A, Beccia V, Di Bello A, Bagalà C, Bensi M, Barone D, Trovato G, Caira G, et al. Comparison of first-line chemotherapy regimens in unresectable locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2024;25(12):1655–1665. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

