Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Subacute Myocarditis
- PMID: 41049904
- PMCID: PMC12489958
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.91464
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Subacute Myocarditis
Abstract
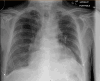
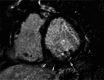
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are a novel class of drugs that direct the immune system to destroy cancer cells, thereby significantly improving patient survival rates. ICI-induced myocarditis, though uncommon, is the most severe side effect associated with these treatments because of its high mortality rate. We report the case of an 81-year-old man with a medical history significant for non-small cell lung cancer who had previously undergone chemoradiotherapy and was receiving the ICI durvalumab. He presented with progressive shortness of breath, and his clinical picture was complicated by pneumonia. His laboratory workup showed evidence of acute kidney injury, elevated liver enzymes, and volume overload. His echocardiogram showed evidence of systolic dysfunction. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmed the diagnosis of subacute myocarditis, likely caused by the ICI. The main presenting symptoms of ICI-induced subacute myocarditis are arrhythmia and heart failure based on the time interval from the initiation of ICI treatment to the onset of symptoms. Our case could have easily been misdiagnosed as a type 2 myocardial infarction because of the patient's pneumonia. Cardiac MRI was the diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of ICI-induced subacute myocarditis in our case. Myocarditis should be considered in patients receiving ICIs, particularly those undergoing combination therapy, because it can be misdiagnosed as a type 2 myocardial infarction.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; ici; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse events; myocarditis.
Copyright © 2025, Al Janabi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Rheumatic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ghosh N, Bass AR. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2022.02.002. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48:411–428. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
