Modern Endophthalmitis Control: The Complete Early Vitrectomy for Endophthalmitis (CEVE) Protocol and Surgical Prophylaxis
- PMID: 41049958
- PMCID: PMC12491984
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.91513
Modern Endophthalmitis Control: The Complete Early Vitrectomy for Endophthalmitis (CEVE) Protocol and Surgical Prophylaxis
Abstract
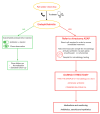
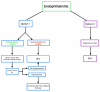
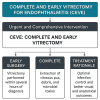
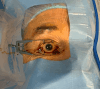
This article presents an overview of endophthalmitis, a severe intraocular inflammatory condition that can develop following surgery, intravitreal injections (IVIs), or ocular trauma. Endogenous cases may also arise, particularly in patients with compromised immune systems. A broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, can be involved, with some displaying high virulence. Given the rapid progression and potential for vision-threatening complications or systemic involvement such as sepsis, immediate and appropriate intervention is essential. Surgical management, especially vitrectomy, plays a central role in treatment. The Complete Early Vitrectomy for Endophthalmitis (CEVE) protocol has demonstrated high effectiveness, particularly when integrated into outpatient ophthalmic surgical practices. This review describes the protocol's practical application in such settings. In addition, it discusses preventive strategies for ocular surgery and injections, with a particular focus on the judicious use of antimicrobial agents. Incorrect antibiotic use, including unnecessary prescribing, inadequate dosing, or prolonged treatment, remains a leading contributor to the development of antimicrobial resistance and warrants critical evaluation. In summary, the CEVE approach appears to offer broad efficacy across different causes of endophthalmitis. Povidone-iodine (PI) remains the most effective agent for perioperative antisepsis. The use of prophylactic antibiotics should be confined to brief, high-potency topical therapy following intraocular procedures, including cataract surgery and phacovitrectomy. Current evidence does not support the routine use of prophylactic antibiotics after intravitreal injections due to minimal benefit and the risk of promoting resistant organisms.
Keywords: antibiotics; endophthalmitis; management algorithm; ocular surgery; povidone-iodine; prevention; vitrectomy.
Copyright © 2025, Kudasiewicz-Kardaszewska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Kuhn F. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2016. Vitreoretinal Surgery: Strategies and Tactics.
-
- Complete and early vitrectomy for endophthalmitis. Morris RE, Kuhn F. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2021;31:2794–2795. - PubMed
-
- International practice patterns for the management of acute postsurgical and postintravitreal injection endophthalmitis: European Vitreo-Retinal Society Endophthalmitis Study Report 1. Soliman MK, Gini G, Kuhn F, et al. Ophthalmol Retina. 2019;3:461–467. - PubMed
-
- Urgent vitrectomy with vancomycin infusion, silicone oil endotamponade, and general antibiotic treatment in multiple cases of endophthalmitis from a single day of intravitreal injections—case series. Pietras-Baczewska A, Jasińska E, Toro MD, et al. https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/10/5/1059/htm. J Clin Med. 2021;10:1059. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vancomycin in infusion during vitrectomy in surgical treatment of acute postoperative and posttraumatic endophthalmitis. Rejdak R, Choragiewicz T, Kalinowska A, et al. https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-016-1830-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:496. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
