Aspergillus Endocarditis: A Rare but Serious Complication During Treatment With Ibrutinib
- PMID: 41050561
- PMCID: PMC12490917
- DOI: 10.1155/crdi/6863015
Aspergillus Endocarditis: A Rare but Serious Complication During Treatment With Ibrutinib
Abstract
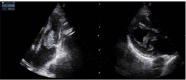
Background: Aspergillus endocarditis (AE) is a rare but life-threatening form of infective endocarditis, accounting for only 0.2% of cases. Despite antifungal and surgical treatment, AE remains a major diagnostic and therapeutic challenge with high mortality rates. Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), has been associated with early-onset invasive aspergillosis. However, no cases of AE have been documented in patients undergoing ibrutinib therapy to date. Case Presentation: A 71-year-old man with relapsed CLL on third-line ibrutinib therapy and a history of arrhythmic cardiomyopathy requiring an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) presented with a six-month history of fever, cough, and fatigue. On admission, a full-body computed tomography scan revealed intestinal ischemia and multiple thrombotic occlusions involving the kidney, spleen, and iliac artery. Markedly elevated beta-D-glucan and serum galactomannan levels prompted empirical initiation of isavuconazole. Transthoracic echocardiography identified a large vegetation (2.5 × 4 cm) on the mitral valve with ICD lead involvement. Despite urgent surgical intervention-including ICD extraction and mitral valve replacement-the patient succumbed to complications. Intraoperative valve cultures grew Aspergillus fumigatus. Conclusions: This report underscores the severity of AE despite combined surgical and antifungal therapy. Given its high mortality rates, clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for AE, particularly in immunocompromised patients or those with a history of cardiac surgery or implanted cardiac devices. Early recognition and aggressive intervention remain essential to improving outcomes.
Keywords: Aspergillus endocarditis; case report; fungal endocarditis; ibrutinib; immunocompromised host.
Copyright © 2025 Luca Mezzadri et al. Case Reports in Infectious Diseases published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gould F. K., Denning D. W., Elliott T. S., et al. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Endocarditis in Adults: A Report of the Working Party of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy . 2012;67(2):269–289. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr450. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

