An interleukin-27-centered cytokine circuit regulates macrophage and T cell interactions in autoimmune diabetes
- PMID: 41050931
- PMCID: PMC12494592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113537
An interleukin-27-centered cytokine circuit regulates macrophage and T cell interactions in autoimmune diabetes
Abstract
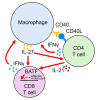
In the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of autoimmune diabetes, interleukin (IL)-27 stimulates interferon γ (IFNγ) production by CD4 and CD8 T cells and is essential for disease development. Here, we tested the role of IL-27 in cellular communication. Single-cell RNA sequencing and T cell adoptive transfer showed that IL-27 intrinsically controlled the differentiation of islet-infiltrating CD4 T cells by driving them toward an IL-21+ Th1 phenotype. Consequently, IL-27 signaling in CD4 T cells was important for BATF and granzyme B expression in islet CD8 T effectors. BATF overexpression increased the diabetogenic potential of β cell autoreactive CD8 T cells lacking help from CD4 T cell-derived IL-21. Macrophages were the main source of IL-27 in the islets, whose expression correlated with T cell infiltration. IFNγ and CD40 signaling conferred by activated T cells induced macrophage IL-27 production. Collectively, our findings reveal a role for IL-27 in orchestrating interconnected positive feedback loops involving CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and macrophages in autoimmune diabetes.
Keywords: Components of the immune system; Immune response; Immune system disorder.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

