BAF60a-dependent chromatin remodeling preserves β cell function and contributes to the therapeutic benefits of GLP-1R agonists
- PMID: 41052246
- PMCID: PMC12646663
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI177980
BAF60a-dependent chromatin remodeling preserves β cell function and contributes to the therapeutic benefits of GLP-1R agonists
Abstract
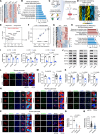
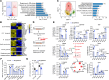
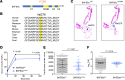
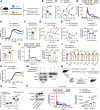
Impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) is a hallmark of β cell dysfunction in diabetes. Epigenetic mechanisms govern cellular glucose sensing and GSIS by β cells, but they remain incompletely defined. Here, we found that BAF60a functions as a chromatin regulator that sustains biphasic GSIS and preserves β cell function under metabolic stress conditions. BAF60a was downregulated in β cells from obese and diabetic mice, monkeys, and humans. β cell-specific inactivation of BAF60a in adult mice impaired GSIS, leading to hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. Conversely, restoring BAF60a expression improved β cell function and systemic glucose homeostasis. Mechanistically, BAF60a physically interacted with Nkx6.1 to selectively modulate chromatin accessibility and transcriptional activity of target genes critical for GSIS coupling in islet β cells. A BAF60a V278M mutation associated with decreased β cell GSIS function was identified in human donors. Mice carrying this mutation, which disrupted the interaction between BAF60a and Nkx6.1, displayed β cell dysfunction and impaired glucose homeostasis. In addition, GLP-1R and GIPR expression was significantly reduced in BAF60a-deficient islets, attenuating the insulinotropic effect of GLP-1R agonists. Together, these findings support a role for BAF60a as a component of the epigenetic machinery that shapes the chromatin landscape in β cells critical for glucose sensing and insulin secretion.
Keywords: Beta cells; Cell biology; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Insulin.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

