EgoVision a YOLO-ViT hybrid for robust egocentric object recognition
- PMID: 41053140
- PMCID: PMC12501230
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-18341-y
EgoVision a YOLO-ViT hybrid for robust egocentric object recognition
Abstract
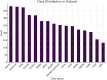
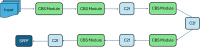
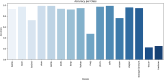
The rapid advancement of egocentric vision has opened new frontiers in computer vision, particularly in assistive technologies, augmented reality, and human-computer interaction. Despite its potential, object recognition from first-person perspectives remains challenging due to factors such as occlusion, motion blur, and frequent viewpoint changes. This paper introduces EgoVision, a novel and lightweight hybrid deep learning framework that fuses the spatial precision of YOLOv8 with the global contextual reasoning of Vision Transformers (ViT). This research presents EgoVision, a whole new hybrid framework combining YOLOv8 with Vision Transformers for object classification in static egocentric frames. The static images come from the HOI4D dataset. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a fused architecture is applied for static object recognition on HOI4D, specifically for real-time use in robotics and augmented reality applications. The framework employs a key-frame extraction strategy and a feature pyramid network to efficiently handle multiscale spatial-temporal features, significantly reducing computational overhead for real-time applications. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoVision outperforms existing models across multiple metrics, achieving up to 99% accuracy on complex object classes such as 'Kettle' and 'Chair', while maintaining high efficiency for deployment on wearable and edge devices. The results establish EgoVision as a robust foundation for next-generation egocentric AI systems.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









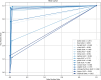
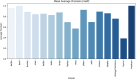
References
-
- Nunez-Marcos, A. Azkune, G. & Arganda-Carreras, I. Egocentric vision-based action recognition: A survey. Neurocomputing472, 175–197. 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.081 (2022).
-
- Li, X. et al. Challenges and trends in egocentric vision: A survey. arXiv preprintarXiv:2503.15275 (2025).
-
- Lowe, D. G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis.60, 91–110 (2004).
-
- Dalal, N. & Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), vol. 1, 886–893. 10.1109/CVPR.2005.177 (2005).
-
- Bishop, C. M. Pattern recognition and machine learning. In Inf. Sci. Stat. 1st edn (Springer, New York, NY, 2006).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

