Beneficial and detrimental consequences of AHR activation in intestinal infection
- PMID: 41057229
- PMCID: PMC12504769
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202503414
Beneficial and detrimental consequences of AHR activation in intestinal infection
Abstract
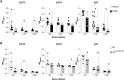
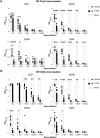
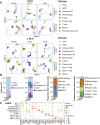
The ligand-dependent transcription factor aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is an environmental sensor whose activation can have physiologically beneficial or detrimental consequences for host immune responses depending on the ligand. Here, we investigated the hypothesis that prolonged AHR activation either because of inefficient ligand metabolism or because of genetic manipulation may underlie the distinction between beneficial and detrimental effects. Our data indicate that prolonged AHR activation caused toxic endpoints for liver and thymus but was not per se interfering with the host response to infection with the intestinal pathogen C. rodentium Genetically driven constitutive AHR activation improved resistance to infection, whereas prolonged AHR activation by the pollutant TCDD resulted in delayed clearance of C. rodentium associated with a suppression in antibody production. Combined single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq analysis provided evidence that TCDD, but not genetic AHR activation, negatively affected dendritic cell functions such as activation, maturation, and antigen presentation. Thus, the detrimental impact of environmental pollutants such as TCDD on immune responses cannot solely be attributed to aberrantly prolonged activation of AHR.
© 2025 Diaz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures









Update of
-
Beneficial and detrimental consequences of AHR activation in intestinal infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 1:2025.05.28.656570. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656570. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Oct 7;8(12):e202503414. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202503414. PMID: 40502009 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Akkaya M, Akkaya B, Sheehan PW, Miozzo P, Pena M, Qi CF, Manzella-Lapeira J, Bolland S, Pierce SK (2017) T cell-dependent antigen adjuvanted with DOTAP-CpG-B but not DOTAP-CpG-A induces robust germinal center responses and high affinity antibodies in mice. Eur J Immunol 47: 1890–1899. 10.1002/eji.201747113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderton MJ, Manson MM, Verschoyle RD, Gescher A, Lamb JH, Farmer PB, Steward WP, Williams ML (2004) Pharmacokinetics and tissue disposition of indole-3-carbinol and its acid condensation products after oral administration to mice. Clin Cancer Res 10: 5233–5241. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0163 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
