E3 Ubiquitin ligases Cbl-b and c-Cbl maintain the homeostasis of macrophages by regulating the M-CSF/M-CSFR signaling axis
- PMID: 41057360
- PMCID: PMC12504418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-08047-4
E3 Ubiquitin ligases Cbl-b and c-Cbl maintain the homeostasis of macrophages by regulating the M-CSF/M-CSFR signaling axis
Abstract
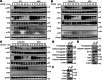
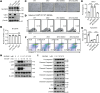
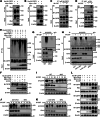
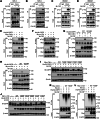
The Casitas B-lineage lymphoma (Cbl) family proteins are E3 ubiquitin ligases implicated in the regulation of various immune cells. However, their function in macrophages remains unclear. Here, we identify both Cbl-b and c-Cbl (Cbls) as inhibitors of macrophage proliferation and promoters of macrophage apoptosis. Mechanically, we identify that Cbls functions upstream of AKT and Erk to mediate the ubiquitination and degradation of M-CSFR. M-CSF stimulation promotes dimerization and autophosphorylation activation of M-CSFR on the macrophage membrane, thereby activating downstream PI3K-AKT and Erk signaling pathways, leading to different biological effects such as macrophage proliferation and survival. At the same time, the Y559 site of the M-CSFR undergoes autophosphorylation, which can promote receptor recruitment and phosphorylation of Cbls. This promotes Cbls to induce K63-linked polyubiquitination at the K791 site of M-CSFR, leading to internalization and degradation of M-CSFR through lysosomal pathways, preventing excessive activation of the signaling pathway. Furthermore, Cbls deficiency results in increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis of macrophages in vitro and in vivo and dKO mice spontaneously develop a macrophage-dominated pulmonary enlargement. Together, these data demonstrate that Cbls play critical roles in the regulation of macrophage homeostasis by inhibiting M-CSFR-mediated AKT and Erk activation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Martinez FO, Helming L, Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:451–83. - PubMed
-
- Kopf M, Schneider C, Nobs SP. The development and function of lung-resident macrophages and dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:36–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82071765/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81771667/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81970027/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82170012/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82370020/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

