Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: effects on thyroid cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling
- PMID: 41057823
- PMCID: PMC12505858
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02470-z
Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: effects on thyroid cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling
Abstract
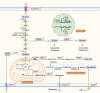
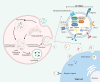
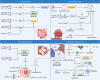
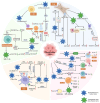
Metabolic reprogramming is one of the fundamental characteristics of thyroid cancer (TC), which meets its energy and biosynthetic demands through mitochondrial dysfunction, glycolysis activation, lipid metabolism imbalance, and glutamine dependency, thereby promoting metastasis and reshaping the immune microenvironment. Exosomes, as extracellular vesicles, play a crucial role in TC by delivering bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. In the tumor microenvironment (TME) of TC, exosomes secreted by both tumor and non-tumor cells interact with each other, driving metabolic reprogramming and forming a bidirectional regulatory network. This significantly alters the biological characteristics of TC cells, including proliferation, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and the acquisition of drug resistance and immune tolerance, ultimately influencing the process of immune escape in TC. This review systematically summarizes how exosomes in the TME of TC promote tumor progression through metabolic reprogramming, providing new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for patients with locally advanced, radioiodine-refractory TC.
Keywords: Exosomes; Immune escape; Metabolic reprogramming; Thyroid cancer; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Li S, et al. Emerging role of metabolic reprogramming in the immune microenvironment and immunotherapy of thyroid cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;144:113702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

