CD8+ T-NK cell crosstalk establishes preemptive immunosurveillance to eliminate antigen-escape tumors
- PMID: 41058706
- PMCID: PMC12497863
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593913
CD8+ T-NK cell crosstalk establishes preemptive immunosurveillance to eliminate antigen-escape tumors
Abstract
Background and objective: Tumor antigen-escape variants undermine immunotherapy by subverting lymphocyte effector functions and reshaping tumor-immune dynamics. It is essential to delineate functional interplay within immune networks during tumor progression. We investigated whether homeostatic crosstalk between CD8+T cells and natural killer (NK) cells preempts tumor antigen-escape.
Methods: Adoptive CD8+T cell transfers were administered before (D-7, homeostatic pre-priming) or after (D+1) tumor establishment in Rag1-/- and Rag1-/-γc-/- mice. Antigen presentation, immune activation, proliferation, cytotoxicity, and memory were quantified by flow cytometry, live bioluminescence and confocal imaging. Monoculture, co-culture, and a 3D silica nanofiber carpet mimicking basement-membrane-like topography modeled intercellular interactions. Signaling arrays and motion metrics (Speed-Distance Index, deceleration) were conducted. Human ligand-receptor pairs engaged in CD8+T-NK crosstalk were probed in silico.
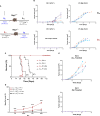
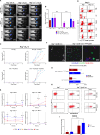
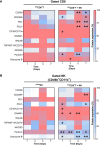
Results and discussion: Pre-tumor D-7 CD8+T cell transfer completely suppressed antigen-escape tumors with NK cells as major effectors showing elevated CD25, CD69, CD107a, and GzmB, marking activated and effector phenotype, and promoting central-memory CD62L⁺CD44⁺CD8⁺TCM precursors. By contrast, post-tumor D+1-transferred CD8+T cells allowed emergence of tumor variants resistant to antigen-specific cytolysis as assessed on day 25, despite those T cells retaining higher intrinsic cytotoxic capacity than the D-7 T cell cohort. Mechanistically, CD8+T and NK cells formed stable contacts through pseudopodial intercellular nanotubes enabling bidirectional membrane exchange and signaling via STAT, Akt, and mTOR pathways, augmenting NK effector function and promoting CD8+TCM differentiation. In silico analysis identified human ligand-receptor pairs engaged in CD8+T-NK adhesion, stimulatory and regulatory axes, including CD200-CD200R, PD-L1-PD-1, and CD18/CD11a-DNAM-1 (CD226). Together, data support a three-phase model of preemptive immunosurveillance initiated by early CD8⁺T-NK crosstalk.
Conclusion: Homeostatic conditioning and effector cooperativity between CD8+T and NK cells protect against tumor immune escape. The findings uncover a mechanistic axis of preemptive immunosurveillance that lays the foundation for next-generation preventive immunotherapies to control antigen-escape tumors.
Keywords: CD8+ T lymphocytes; T cell–NK cell cooperativity; adoptive cell transfer; antigen-loss variants; cancer immunotherapy; membranous tunneling nanotubes; preemptive immunosurveillance; tumor immune escape.
Copyright © 2025 Uzhachenko, González Ochoa, Kanagasabai, Rajakaruna, Thounaojam, de Aquino, Rana, Costa, Terekhov, Hofmeister, Sayers, Boyer, Ivanova, Goodwin, Schmitt-Verhulst and Shanker.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors TS and AS were employed by Science Applications International Corporation, Inc., and Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

