Long Term Outcomes of Lung Transplantation in Sensitized Patients Following Eculizumab Use With the Desensitization Protocol
- PMID: 41058980
- PMCID: PMC12497660
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2025.15040
Long Term Outcomes of Lung Transplantation in Sensitized Patients Following Eculizumab Use With the Desensitization Protocol
Abstract
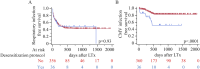
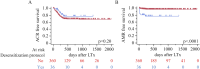
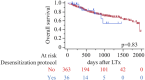
Lung transplantation remains a life-saving option for end-stage pulmonary diseases, but sensitized patients with anti HLA antibodies carry high risk; recent desensitization advances, such as eculizumab, may permit outcomes comparable to non-sensitized recipients with tailored perioperative care. In this prospective cohort study of 399 adult lung transplant recipients, 36 sensitized patients underwent a protocol combining preoperative plasmapheresis, a defined eculizumab regimen, anti-thymocyte globulin, and IVIG. In comparison, 363 non-sensitized recipients received standard immunosuppression. We compared recipient/donor characteristics, intraoperative parameters, and postoperative outcomes, including primary graft dysfunction, infection, rejection, and overall survival. Desensitized patients were older, predominantly female, and had significantly higher panel reactive antibody levels and preformed donor-specific antibodies; intraoperatively, they required more blood transfusions and VA-ECMO support. Postoperatively, they exhibited higher rates of de novo donor-specific antibodies, antibody-mediated rejection, longer ICU stays, increased dialysis requirement, and more frequent CMV infections. Despite these differences, rates of acute cellular rejection, chronic lung allograft dysfunction, and one-year and overall survival were similar between groups. Our findings suggest that lung transplantation in sensitized patients managed with a desensitization protocol, including eculizumab, is feasible and safe, achieving outcomes comparable to those of non-sensitized recipients.
Keywords: ACR; AMR; eculizumab; lung transplantation; sensitized.
Copyright © 2025 Miyashita, Kaiho, Pinelli, Joudi, John, Chang, Thomae, Kamar, Atkinson, Bharat, Budinger, Arunachalam and Kurihara.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Iyer HS, Jackson AM, Montgomery RA. Sensitized Patients, Transplant, and Management. Curr Transpl Rep (2014) 1(2):69–77. 10.1007/s40472-014-0010-0 - DOI
-
- Kahwaji J, Choi J, Vo A, Jordan SC. Immunologic and Infectious Complications in Highly Sensitized Patients Post-kidney Transplantation. Clin Transpl (2015) 31:265–73. - PubMed
-
- Habli M, Belal D, Sharma A, Halawa A. Transplanting Highly Sensitized Patients. J The Egypt Soc Nephrol Transplant (2023) 23(2):45–52. 10.4103/jesnt.jesnt_34_22 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

