The association of the atherogenic index of plasma with hypertension, diabetes, and their comorbidities in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people: a cross-sectional study from CHARLS
- PMID: 41058994
- PMCID: PMC12497758
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1607601
The association of the atherogenic index of plasma with hypertension, diabetes, and their comorbidities in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people: a cross-sectional study from CHARLS
Abstract
Background: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is acknowledged as a contemporary indicator of insulin resistance. Previous research on AIP and metabolism-related diseases was limited and primarily concentrated on individual diseases. The aim of this investigation was to systematically examine the relationship among AIP and hypertension, diabetes, and their comorbidities.
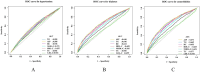
Methods: This study employed a cross-sectional design. Using data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) of 2011, we conducted a systematic investigation of the association between AIP and the risk of hypertension, diabetes, and their comorbidities through restricted cubic spline plots (RCS) and multiple multivariate logistic regression. Additionally, receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) were employed to assess AIP's predictive validity for these conditions.
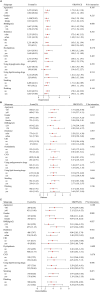
Results: This study comprised 8,450 participants, with an average age of 59.57 years. The prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and their comorbidities were 40.98, 15.62, and 8.52%, respectively. The RCS demonstrated a non-linear positive correlation between the AIP and these disorders. For each unit increased in AIP, the risk of hypertension, diabetes, and comorbidities elevated by 0.63-fold, 2.55-fold, and 2.75-fold, respectively. The ROC analysis demonstrated that AIP outperformed traditional lipid parameters in predicting both diabetes and comorbidities risk (AUC: 0.6465, 0.6725).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that heightened AIP was strongly linked to a high risk of hypertension, diabetes, and comorbidities among middle-aged and elderly Chinese individuals.
Keywords: CHARLS; atherogenic index of plasma; comorbidities; diabetes; hypertension.
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Zhang, Zeng and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

