Cholesterol-lowering drug targets reduce risk of dementia: Mendelian randomization and meta-analyses of 1 million individuals
- PMID: 41059729
- PMCID: PMC12505197
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70638
Cholesterol-lowering drug targets reduce risk of dementia: Mendelian randomization and meta-analyses of 1 million individuals
Abstract
Introduction: We tested whether genetically proxied non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C)-lowering drug targets reduce risk of all-cause dementia.
Methods: We included 1,091,775 individuals from three prospective general population cohorts with individual-level data and two consortia with summary-level data. We selected genetic variants within HMGCR, NPC1L1, PCSK9, ANGPTL4, LPL, and CETP associated with non-HDL-C. These variants were used as exposures in Cox regression and one- and two-sample Mendelian randomization. Results were meta-analyzed.
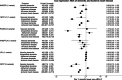
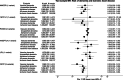
Results: Meta-analysis of one-sample Mendelian randomization odds ratios per 1 mmol/L (39 mg/dL) lower non-HDL-C was 0.24 (0.18-0.31) for HMGCR, 0.18 (0.12-0.25) for NPC1L1, 0.97 (0.70-1.35) for PCSK9, 1.66 (0.52-5.36) for ANGPTL4, 1.41 (0.63-3.16) for LPL, and 0.30 (0.26-0.34) for CETP. Cox regression and two-sample Mendelian randomization results were mostly directionally consistent.
Discussion: Genetic lowering of non-HDL cholesterol via HMGCR, NPC1L1, and CETP reduces the risk of dementia. This reflects the effect of lifelong differences in non-HDL cholesterol on risk of dementia.
Highlights: Variants in HMGCR, NPC1L1, and CETP reduce the risk of dementia via non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C). An effect of PCSK9, ANGPTL4, and LPL variants on dementia risk cannot be excluded. This reflects the effect of lifelong lower non-HDL-C on risk of dementia.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; Niemann‐Pick C1‐like 1; atherosclerosis; cholesterol; cholesteryl ester transfer protein; dementia; genetics; lipid lowering; lipoproteins; β‐hydroxy β‐methylglutaryl‐CoA reductase.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
B.G.N. reports consultancies/talks for AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Amgen, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, Abbott, Ultragenyx, USV, Lilly, Arrowhead, and Marea. V.W. reports support from the UK Medical Research Council Integrative Epidemiology Unit (MC_UU_00032/03), grants from Horizon; “EU PROACT: A European proactive adaptive clinical trials network,” NIHR; “Evaluation of COVID‐19 vaccine products and schedules,” NIHR; “Impact and inequalities of winter pressures in primary care: providing the evidence base for mitigation strategies”; and honoraria for presentation at the 2nd International Conference on High‐Quality Healthy Ageing in Beijing. G.D.S. reports grants from the Medical Research Council and scientific advisory board membership for Bristol Myers Squibb, Relation Therapeutics, and Insitro. Other authors have no relevant financial or non‐financial interests to disclose. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

