TRAF6 integrates innate immune signals to regulate glucose homeostasis via Parkin-dependent and Parkin-independent mitophagy
- PMID: 41061082
- PMCID: PMC12507004
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adw4153
TRAF6 integrates innate immune signals to regulate glucose homeostasis via Parkin-dependent and Parkin-independent mitophagy
Abstract
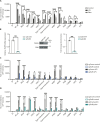
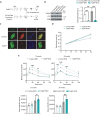
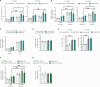
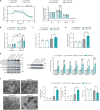
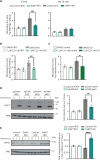
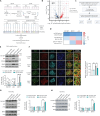
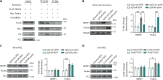
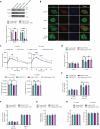
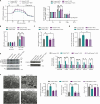
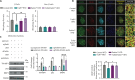
Innate immune signaling is activated in immunometabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, yet its impact on glucose homeostasis is controversial. Here, we report that the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 integrates innate immune signals following diet-induced obesity to promote glucose homeostasis through the induction of mitophagy. Whereas TRAF6 was dispensable for pancreatic β cell function at baseline, TRAF6 was pivotal for insulin secretion, mitochondrial respiration, and mitophagy following metabolic stress in mouse and human islets. TRAF6 was critical for the recruitment and function of the ubiquitin-mediated (Parkin-dependent) mitophagy machinery. Glucose intolerance induced by TRAF6 deficiency following metabolic stress was reversed by concomitant Parkin deficiency by relieving obstructions in receptor-mediated (Parkin-independent) mitophagy. Our results establish that TRAF6 is vital for traffic through Parkin-mediated mitophagy and implicates TRAF6 in the cross-regulation of ubiquitin- and receptor-mediated mitophagy. Together, we illustrate that β cells engage innate immune signaling to adaptively respond to a diabetogenic environment.
Figures
Update of
-
TRAF6 integrates innate immune signals to regulate glucose homeostasis via Parkin-dependent and-independent mitophagy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Sep 5:2025.01.31.635900. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.31.635900. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Oct 10;11(41):eadw4153. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adw4153. PMID: 39974969 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, P. Walter, “Innate immunity” in Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th Edition (Garland Science, 2002); https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26846/.
-
- Kim S.-J., Choi Y., Choi Y.-H., Park T., Obesity activates toll-like receptor-mediated proinflammatory signaling cascades in the adipose tissue of mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 23, 113–122 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AG000114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK138544/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK135032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK136671/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM145304/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108921/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127270/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007413/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK142799/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK133533/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK135268/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK127747/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004444/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

