When a model gives you mixed signals: cognitive effects and visual behavior
- PMID: 41064266
- PMCID: PMC12500769
- DOI: 10.1007/s44311-025-00022-8
When a model gives you mixed signals: cognitive effects and visual behavior
Abstract
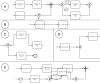
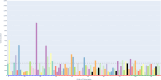
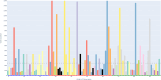
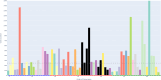
Ambiguity in business process models can result in multiple interpretations by model readers. This leads to undesirable outcomes such as misunderstandings, unclear allocation of responsibilities, and unexpected behaviors. Despite these potential consequences, the impact of ambiguity on model readers has received limited attention so far. This article presents an eye-tracking study designed to investigate the effects of various types of ambiguity (i.e., layout, semantic, syntactic, and lexical) on readers' cognitive load, comprehension, and visual associations while interpreting process models. In addition, the study delves into the behaviors of model readers when resolving ambiguity in process models. These behaviors are investigated following a qualitative approach combining both eye-tracking and think-aloud data. The results demonstrate that ambiguities significantly influence cognitive load, comprehension, and visual associations, emphasizing the negative effects of ambiguity. Moreover, the qualitative insights suggest that participants exhibit specific behaviors when trying to resolve ambiguities. These findings underscore the need for advanced mechanisms to detect and mitigate ambiguity in process models.
Keywords: Ambiguity; Cognitive load; Eye-tracking; Process models; Visual behavior.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Abbad-Andaloussi A, Burattin A, Slaats T et al (2023a) Complexity in declarative process models: metrics and multi-modal assessment of cognitive load. Expert Syst Appl 233:120924
-
- Abbad-Andaloussi A, Lübke D, Weber B (2023b) Conducting eye-tracking studies on large and interactive process models using eyemind. SoftwareX 24:101564
-
- Abbad-Andaloussi A, Schreiber C, Weber B (2024) Using eye-tracking to detect search and inference during process model comprehension. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Cooperative Information Systems (in press)
-
- Abbad-Andaloussi A, Zerbato F, Burattin A et al (2021) Exploring how users engage with hybrid process artifacts based on declarative process models: a behavioral analysis based on eye-tracking and think-aloud. Softw Syst Model 20:1437–1464
-
- Aggarwal CC (2015) Data mining: the textbook. Springer
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
