Comparative Efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Moderate-to-Severe Crohn's Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 41064350
- PMCID: PMC12503645
- DOI: 10.1159/000547707
Comparative Efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Moderate-to-Severe Crohn's Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors have emerged as promising therapeutic options for moderate-to-severe Crohn's disease (CD), but comparative data between agents remain limited. This study aimed to assess and rank the efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors across key clinical and endoscopic outcomes using network meta-analysis.
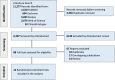
Methods: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating IL-12/23 (ustekinumab) and IL-23 inhibitors (risankizumab, mirikizumab, guselkumab, briakinumab, and MEDI2070) versus placebo or each other in adult patients with moderate-to-severe CD. Primary outcomes included clinical and endoscopic remission (assessed at the end of the induction and maintenance phases) and corticosteroid-free clinical remission (assessed at the end of the maintenance phase). Risk ratios (RRs) were estimated using a random-effects model. All analyses were conducted in R using the netmeta package. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) analysis was used to rank treatments across these endpoints.
Results: Fourteen RCTs involving 4,464 patients during the induction phase and 2,601 patients during the maintenance phase were included. Guselkumab achieved the highest clinical remission rate compared to placebo at the end of both the induction phase (RR = 2.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.03-3.39; SUCRA: 91%) and the maintenance phase (RR = 2.37; 95% CI, 1.64-3.42; SUCRA: 85%). In addition, guselkumab was superior to mirikizumab in terms of clinical remission at the end of the induction phase (RR = 1.66; 95% CI, 1.16-2.37). Guselkumab was also the most effective agent for achieving corticosteroid-free clinical remission compared to placebo (RR = 3.06; 95% CI, 1.52-6.16; SUCRA: 78%) at the end of the maintenance phase. Mirikizumab achieved the highest endoscopic remission rate compared to placebo at the end of both the induction phase (RR = 3.52; 95% CI, 1.50-8.27; SUCRA: 78%) and the maintenance phase (RR = 5.84; 95% CI, 2.76-12.37; SUCRA: 88%). Furthermore, mirikizumab, guselkumab, and risankizumab were superior to ustekinumab in terms of endoscopic remission at the end of the maintenance phase.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that guselkumab may be a potential first-line therapy for patients presenting with predominant clinical symptoms, offering the additional benefit of reducing corticosteroid use and its associated long-term risks. Conversely, mirikizumab may be the preferred option for patients with persistent mucosal inflammation, owing to its superior efficacy in achieving endoscopic remission.
Keywords: Corticosteroid-free remission; Crohn’s disease; Endoscopic remission; IL-12/23 inhibitors; IL-23 inhibitors; Network meta-analysis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Crohn’s disease. Lancet. 2012;380(9853):1590–605. - PubMed
-
- Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet. 2017;389(10080):1741–55. - PubMed
-
- Chang JT. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel diseases. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2652–64. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen GC, Loftus EV Jr, Hirano I, Falck-Ytter Y, Singh S, Sultan S, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on the management of Crohn’s disease after surgical resection. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):271–5. - PubMed
-
- Pariente B, Hu S, Bettenworth D, Speca S, Desreumaux P, Meuwis MA, et al. Treatments for Crohn’s disease-associated bowel damage: a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(5):847–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

