PCSK9 Promotes Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability by Inducing VSMC Ferroptosis through the YAP1-NUPR1 Axis
- PMID: 41064368
- PMCID: PMC12501616
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0922
PCSK9 Promotes Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability by Inducing VSMC Ferroptosis through the YAP1-NUPR1 Axis
Abstract
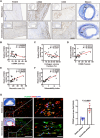
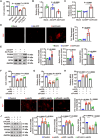
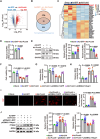
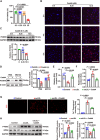
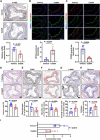
Atherosclerosis persists as a principal driver of global cardiovascular mortality and morbidity, and its sustained prevalence surge fuels the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Plaque instability is a critical determinant of MACE, as fissure formation or rupture of vulnerable plaques can precipitate thromboembolic complications. In this study, we investigate a noncanonical role of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) beyond its lipid regulatory function, focusing on its impact on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in the context of plaque instability. Our results demonstrate that PCSK9 overactivity markedly promotes ferroptotic cell death in VSMCs, thereby exacerbating plaque vulnerability. Furthermore, we delineate the underlying mechanism: PCSK9 physically interacts with Yes-associated protein 1 and targets it for lysosomal degradation, which, in turn, suppresses the expression of nuclear protein 1. In conclusion, our findings unveil a novel role of PCSK9 in promoting plaque instability by driving ferroptosis in VSMCs, suggesting that targeting PCSK9 presents a potential avenue for plaque stabilization, thereby mitigating the incidence of major MACE.
Copyright © 2025 Yuting Cui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

